Complete Guide to PMP ITTO 2024: Learn Inputs, Tools, Techniques, and Outputs
Published:
Updated:

ITTO stands for Inputs, Tools, Techniques, and Outputs. It is a framework used in project management to understand the connections between the resources, information, and plans used to create and implement a project plan.
It refers to the inputs, tools, and techniques used to produce the outputs of each process in the project management life cycle. PMP ITTO helps ensure that project activities and tasks are clearly defined and that the necessary resources and approaches are available to complete them successfully.
For your convenience, we have explained all the common inputs, techniques, tools and outputs that are used in this project management framework.
Common Inputs in Project Management
Inputs in Input-Tool-Technique-Output (ITTO) in project management refer to the resources, information, and documents necessary to complete a specific activity or task. Some common inputs used in ITTO include:
Project Charter
This document outlines the scope, objectives, and stakeholders for the project. It serves as a high-level overview of the project and helps to define its boundaries.
Scope statement
This document defines the project's boundaries and identifies the specific deliverables that will be produced. It helps to ensure that the project stays on track and meets its objectives.
Budget
This is the allocated amount of money that will be used to fund the project. It is important to clearly understand the budget to make sure that the project stays within its financial constraints.
Schedule
This is a timeline that outlines the start and end dates for the project. It helps to ensure that the project stays on track and meets its deadlines.
Stakeholder List
This is a list of individuals or groups that are impacted by or have a vested interest in the project. It is important to identify and engage with stakeholders in order to ensure that the project is aligned with their needs and expectations.
Risk Register
This document identifies potential risks to the project and outlines strategies for mitigating them. It helps project managers manage risk and proactively ensure the project's success.
Resource list
This is a list of the people, equipment, and materials needed to complete the project. It is important to clearly understand the resources needed to plan and execute the project effectively.
Change request
This is a request to modify the project's scope, budget, or schedule. It is important to have a process for managing change requests to ensure that the project stays on track and meets its objectives.
The specific inputs needed will depend on the nature of the project and its goals. It is important to carefully consider the inputs needed for each project in order to ensure that it is successful.
Common Tools in PMP ITTO
Tools in Input-Tool-Technique-Output (ITTO) in project management refer to the processes, techniques, or software used to analyze, plan, or execute a specific activity or task. Some common tools used in ITTO are as follows:
Project Management Software
This computer program helps project managers plan, track, and control projects. It often includes task lists, Gantt charts, resource management, and risk management. Project management software is a useful tool that can help in organizing and coordinating the work of a project team and ensuring that the project stays on track.
Risk Assessment Tools
These are tools or processes used to identify and analyze potential risks to the project. They may include techniques such as risk registers, risk matrices, and risk assessments to help project managers identify, prioritize, and mitigate risks.
Spreadsheets
These computer programs allow users to organize and manipulate data in rows and columns. They are useful tools for analyzing data, creating reports, and tracking progress. Examples are Responsibility and Assignment Matrix (RAM) and probability and impact matrix.
Diagrams
These are visual representations that assist in analysis through data representation. Examples of diagrams are scatter plot, cause and effect diagram, control charts, pareto diagram, and affinity diagram.
Quality Control Tools
These are tools or processes used to ensure that the project meets the established quality standards and criteria. They may include techniques such as inspections, testing, and quality assurance methods to ensure that the final product or service meets the required standards.
Decision-Making Tools
These tools or processes help project managers make informed decisions, such as cost-benefit analysis or the decision tree. They can be useful for analyzing data and considering different options in order to make informed decisions.
Communication Tools
These are tools or processes used to facilitate communication within the project team, such as email, video conferencing, or project management software. The right tools can help to ensure that team members stay connected and informed.
The specific tools used in ITTO will depend on the project's nature and its goals. It is important to choose the appropriate tools that are according to the needs and objectives of the project. By selecting the right tools and using them effectively, project managers can ensure they have the resources and support needed to complete the project successfully.
Common Techniques in PMP ITTO
Techniques in Input-Tool-Technique-Output (ITTO) in project management refer to the specific methods or approaches used to perform a specific activity or task. Some common techniques used in ITTO are as follows:
Brainstorming
This group problem-solving technique involves generating ideas or solutions through free-flowing discussion and collaboration. It is a useful technique for generating different ideas quickly and can be used to identify creative solutions to problems.
Stakeholder Analysis
This technique identifies and prioritizes stakeholders based on their level of interest or influence on the project. It helps project managers understand stakeholders' needs and expectations and develop strategies for engaging with them.
Expert Judgment
This is the use of specialized knowledge or experience to make informed decisions or solve problems. It is often used when there is a need for more data or when the problem requires specialized expertise.
Root Cause Analysis
This technique is used to identify the underlying cause of a problem or issue rather than just treating the symptoms. It is a useful technique for identifying the root cause of a problem and implementing solutions that address the underlying issue.
SWOT Analysis
This technique identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a project or organization. It is useful for assessing the current situation and identifying potential risks and opportunities.
Risk Assessment
This is the process of identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential risks to the project. It helps project managers proactively manage risk and ensure the project's success.
Product Analysis (Quality Control)
This is the process of ensuring that the project meets the established quality standards and criteria. It is a critical part of the project management process. It involves various techniques, such as inspections, testing, and reviews, to ensure that the final product or service meets the required standards.
Agile Methodology Tools & Techniques
Agile methodologies are flexible, iterative approaches to project management that focus on adaptability and continuous improvement. They involve frequent communication, collaboration, and feedback to ensure that the project meets the needs of the stakeholders.
It is important to choose the appropriate techniques based on the needs and objectives of the project. It is also important to consider the skills and resources of the project team when selecting techniques, as some may require specialized training or expertise. Using various techniques, project managers can ensure that they have the tools and approaches needed to complete the project successfully.
Common Outputs in Project Management
Outputs in Input-Tool-Technique-Output (ITTO) in project management refer to the results or deliverables produced due to a specific activity, process, or task. Following are some of the common outputs in ITTO:
Gantt Charts
This group problem-solving technique involves generating ideas or solutions through free-flowing discussion and collaboration. It is a useful technique for generating different ideas quickly and can be used to identify creative solutions to problems.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
This hierarchical representation of a project's scope breaks down the work into smaller, manageable chunks. It helps project managers understand the project's scope and plan and coordinate the work.
Project Deliverables
This is the use of specialized knowledge or experience to make informed decisions or solve problems. It is often used when there is a need for more data or when the problem requires specialized expertise.
Status Reports
These are updates on the project's progress, including any issues or risks encountered. They help project managers track the project's progress and identify any potential problems that need to be addressed.
Approved Changes
These are changes that were approved and involve requests to modify the project's scope, budget, or schedule. It is essential to have a process in place to manage and approve or reject change requests.
Lessons Learned
These documents outline the project's successes and challenges and suggest ways to improve future projects. They help project managers to learn from their experiences and apply those lessons to future projects.
Final Report
This is a document that summarizes the results of the project and includes any recommendations for future work. It helps stakeholders understand the project's outcomes and how it has impacted the organization.
Completed project
This is the final product or result of the project, such as a new product or service. It is the project's end goal and should be clearly defined at the beginning to guide the work and measure its success.
The specific outputs needed will depend on the nature of the project and its goals. It is important to clearly define the outputs at the beginning of the project so they can be used to plan the project and measure its performance.
Process Groups in Project Management
In Input-Tool-Technique-Output (ITTO) in project management, the process groups refer to the phases or stages of a project. The Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide®) identifies five process groups in project management: initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing.
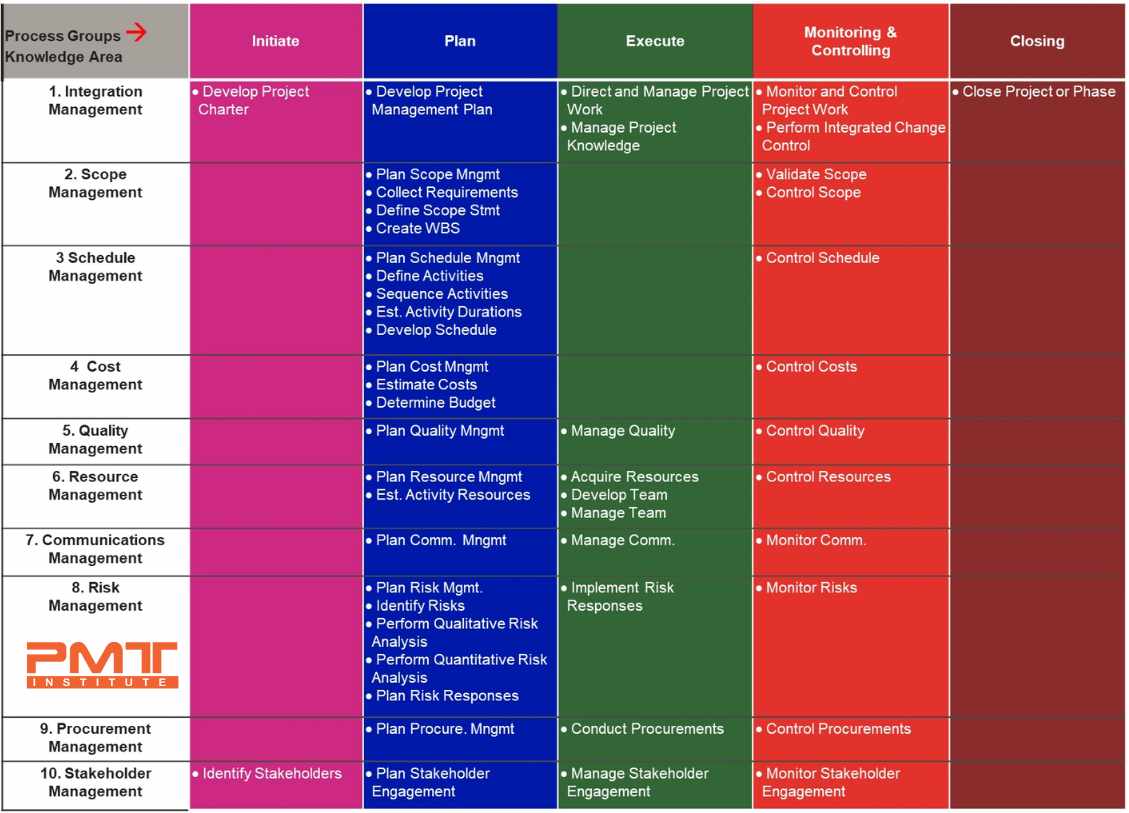
Initiating Process Group
The inputs might include documents such as the project charter and stakeholder list in the initiating process group. The tools might include techniques such as an expert judgment or stakeholder analysis. The techniques used in this process group include brainstorming or root cause analysis to identify the scope and objectives of the project, and the outputs include the project charter and stakeholder list.
Planning Process Group
In this group, the inputs might include the project charter and work breakdown structure. The tools include project management software or decision-making tools. The techniques used in this process group include risk assessment or quality planning tools to define the scope and objectives of the project, develop the quality management plan, and the outputs include the project plan and risk register.
Executing Process Group
In this process group, the inputs might include the project plan and resources, and the tools might include project management software or communication tools. The techniques used in this process group include agile methodologies or collaboration to coordinate the project team's work, and the outputs include the deliverables or interim reports.
Monitoring and Controlling Process Group
In this process group, the inputs might include the project plan and performance data, and the tools might include project management software or quality control tools. The techniques used in this process group include risk assessment or quality control to track the project's progress and identify and address any issues. The outputs might include updated project plans or risk registers.
Closing Process Group
The inputs in this process group might include the final deliverables and acceptance criteria, and the tools might include communication tools or document management systems. The techniques used in this process group include acceptance testing, or lessons learned review to complete the project and document the results. The outputs might include the final report and project closure document.
These process groups provide a framework for organizing and managing the work of a project systematically and effectively. By using the appropriate inputs, tools, techniques, and outputs for each process group, project managers can ensure that they have the resources and approaches needed to complete the project successfully.
Examples to Illustrate ITTO in Action
For your convenience, we have shared some examples that can help in understanding ITTO in PMP in a better way.
Example 1
Imagine you are a project manager tasked with organizing a company retreat.
Inputs
Project charter: This document outlines the scope, objectives, and stakeholders of the project, as well as the authority and responsibility of the project manager.
Budget: This is the amount of money allocated for the retreat.
Venue requirements include the venue's capacity, amenities, and location.
Participant list: This is a list of the employees attending the retreat.
Tools and Techniques
Research (interviews & focus groups): This involves gathering information about potential venues that meet the requirements and budget.
Decision-making tool: You may use a decision matrix to evaluate the pros and cons of each potential venue and choose the one that best meets the needs of the company.
Communication skills: You must communicate effectively with the venue and the participants to ensure everything is organized and smooth.
Outputs
Retreat Agenda: This is a schedule of the activities and events that will take place during the retreat.
Retreat Evaluation: This document assesses the retreat's success and provides feedback for future planning.
In this example, the inputs (project charter, budget, venue requirements, participant list) are used in conjunction with the tools and techniques (research, decision-making tool, communication skills) to produce the outputs (retreat agenda, retreat evaluation).
Example 2
Input: A list of items that need to be purchased for a dinner party (e.g., ingredients, decorations, tableware).
Tool: A shopping list app or spreadsheet to organize the items and track progress.
Technique: A budgeting approach to ensure the items are purchased within the allocated budget.
Output: A successful dinner party with all of the necessary items purchased and in place.
In this example, the input is the list of items that must be purchased for the dinner party. The tool is the shopping list app or spreadsheet that is used to organize and track the items. The technique is the budgeting approach that is used to ensure that the items are purchased within the allocated budget. The output is a successful dinner party with all of the necessary items in place.
Example 3
Imagine you are a project manager at a construction company tasked with building a new office building.
Inputs
Project charter: This document outlines the scope, objectives, and stakeholders of the project, as well as the authority and responsibility of the project manager.
Budget: This is the amount of money allocated to construct the building.
Design plans: These are the drawings and specifications for the building, including the layout, materials, and finishes.
Permits: These are the legal documents allowing the construction to occur.
Tools and Techniques
Construction management software: This tool helps plan, schedule, and track the construction process.
Risk assessment: This involves identifying and evaluating potential risks to the project, such as weather, accidents, or delays.
Change management process: This is a set of procedures for requesting and evaluating changes to the project.
Outputs
Office building: This completed building meets the design plans and budget.
Change requests: These documents outline changes to the project that the project manager and the client have approved.
Status reports: These are documents that provide updates on the progress of the construction and any issues that have arisen.
In this example, the inputs (project charter, budget, design plans, permits) are used in conjunction with the tools and techniques (construction management software, risk assessment, change management process) to produce the outputs (office building, change requests, status reports).
Summary
To sum it up, ITTO is an important concept in project management because it helps project managers understand the inputs, tools, and techniques required to produce the desired outputs of each process in the project management life cycle. It also helps project managers to identify and resolve problems that may arise during the project and adapt to changes in the project environment.
By understanding the relationships between inputs, tools, techniques, and outputs, project managers can ensure they have the necessary resources, information, and plans to complete the project successfully.


