Ultimate Guide to Cost Performance Index (CPI) for Project Success
Published:
Updated:
Do you need help to keep your project on track and within budget? The cost performance index (CPI) may be the key to understanding why your project is overrunning and how you can get it back on track. Understanding the CPI is essential to ensure your project's success.
In order to explain this key metric in project management, we will dive into what CPI is, how it's calculated, and how it can be used to assess the efficiency of your project's spending.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- CPI Calculation: Cost Performance Index (CPI) is calculated as Earned Value (EV) divided by Actual Cost (AC), used to measure cost efficiency.
- Factors Influencing CPI: Scope creep, poor estimation, project management issues, and unforeseen circumstances can impact CPI.
- Uses of CPI: Tracking project progress, evaluating performance, identifying cost overruns, and negotiating with stakeholders.
- Improving CPI: Effective project management, accurate estimation, controlling scope changes, and proactive risk management are key to improving CPI.
What is CPI in Project Management?
Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a critical metric in Project Management that measures the cost efficiency of a project. It helps program managers determine if the project is within budget by comparing the earned value to the actual cost of the project.
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is a metric in project management that helps assess the efficiency of spending on a project. To calculate the CPI, you need to divide the value of work completed (also known as the earned value) by the actual cost incurred to complete that work.
The CPI can be used to assess the overall performance of a project, as well as to find the areas where cost overruns may be occurring. By tracking the CPI over time, project managers will be able to identify trends and take corrective action to keep the project on track and within budget.
How to Calculate CPI in Project Management?
To calculate the CPI, you will need to gather the following information.
The total cost of the project to date: This includes all direct and indirect costs incurred on the project up to the current point in time.
The total budgeted cost for the project: This is the total amount of money that was allocated for the project at the start of the project.
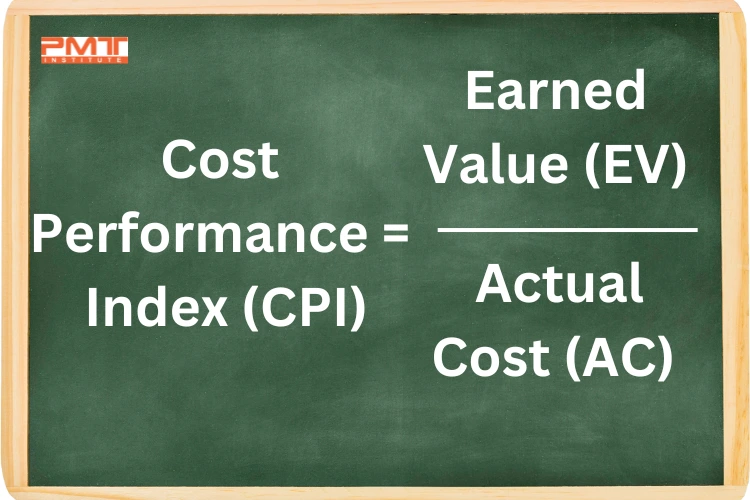
The CPI formula: The CPI is calculated by dividing the project's total cost to date by the total budgeted cost. The project's total cost to date is represented by Earned Value (EV), and the total budgeted cost for the project is represented by Actual Cost (AC), which means the formula of project management CPI is as follows.
To calculate the CPI, use the following formula: CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
Earned Value (EV): The value of work actually performed.
Actual Cost (AC): The total cost incurred for the work performed.
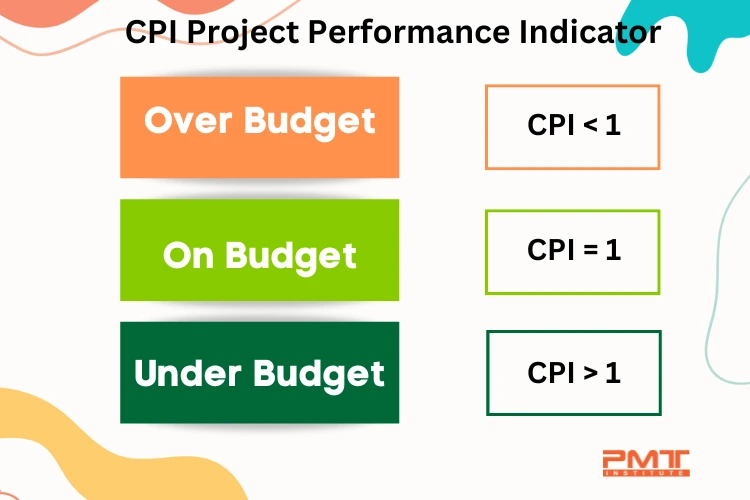
A CPI value of 1 indicates that the project is on budget. A CPI greater than 1 suggests that the project is under budget, while a CPI less than 1 indicates that the project is over budget.
CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
To explain it further, suppose that the total cost of a project to date is $50,000 and the total budgeted cost for the project is $60,000; the CPI would be calculated as follows: CPI = $50,000 / $60,000 = 0.83
The resulting CPI of 0.83 indicates that the project runs at 83% of its budgeted cost. It is important to note that a CPI of less than 1.0 indicates that the project is running over budget, while a CPI of greater than 1.0 indicates that the project is running under budget. On the other hand, CPI = 1 indicates the project is within the budget.
It is essential to understand that the CPI is a lagging indicator, reflecting the project's performance up until the current point. As such, it can be used to predict the project's final cost based on the CPI trend over time. For instance, if the CPI has been consistently above 1.0, the project will likely come in under budget. On the other hand, if the CPI has been consistently below 1.0, the project will likely go over budget.
Examples of Project Management CPI
Following are some of the examples that will let you understand the concept of the Cost Performance Index (CPI).
Example 1: Building a New Office Building
Let's say a construction company is building a new office for a client. The project has a budget of $2 million, and it will take around 18 months to complete. After six months, the construction company has spent $800,000 and has completed work valued at $1 million. The CPI can be calculated as follows:
CPI = Earned Value / Actual Cost
CPI = $1 million / $800,000
CPI = 1.25
In this case, the CPI is 1.25, which indicates that the project is performing efficiently. However, the construction company needs to continue tracking the CPI over time to ensure that the project stays on track and within budget.
Example 2: Renovating a Hotel
Suppose a hotel owner is renovating an existing hotel. The project has a budget of $1 million and is expected to take nine months to complete. After six months, the hotel owner has spent $600,000 and has completed work valued at $700,000. The CPI can be calculated as follows:
CPI = Earned Value / Actual Cost
CPI = $700,000 / $600,000
CPI = 1.17
In this case, the CPI is 1.17, which indicates that the project is performing efficiently. However, the hotel owner needs to continue tracking the CPI over time to ensure that the project stays on track and within budget.
Example 3: Developing a New Software Application
A software development company is working on a new application for a client. The project has a budget of $500,000 and will take 12 months to complete. After three months, the software development company has spent $125,000 and has completed 20% of the work. The CPI can be calculated as follows:
Earned Value = Percent Work Complete x Budget
So, in this case, Earned Value = 20% x 500,000 = 100,000
CPI = Earned Value / Actual Cost
CPI = $100,000 / $125,000
CPI = 0.8
In this case, the CPI is 0.8, which indicates that the project is over budget. This may be due to scope creep, poor estimation, or poor project management. The software development company will need to take action to address the issue and bring the project back on track.
In all of these examples, you can clearly see the importance of CPI in project management and why most project managers rely on this key metric to assess the efficiency of a project and identify areas where cost overruns may occur.
Which Factors Impact the CPI of a Project?
Several factors can impact the CPI of a project which are as follows.
Scope Creep
This occurs when the project scope expands beyond the original scope, leading to additional costs. For instance, if the project scope includes the construction of a new office building, scope creep could occur if the client adds additional features such as a gym or a conference center. These additional features would increase the project's cost and impact the CPI.
Poor Estimation
If the initial estimates for the project are inaccurate, it can lead to cost overruns. This is due to a lack of information, unrealistic assumptions about the project, or simply poor estimation skills.
Poor Project Management
Ineffective project management can lead to delays, which can increase costs. This can happen due to a lack of clear goals and objectives, inadequate communication, or a lack of resources.
Changes in Project Scope
Whether intentional or not, any change to the project scope can impact the CPI. For instance, if the project scope includes the renovation of a hotel, changes to the scope could include adding additional rooms or changing the hotel's design. These changes would increase the cost of the project and impact the CPI.
Unforeseen Circumstances
Unexpected events, such as natural disasters, can impact the CPI. For example, if a project involves the construction of a new office building, and an earthquake destroys the construction site, the project will be delayed, and the cost will increase, impacting the CPI.
Inflation
The general increase in the price level of goods and services over time within an economy is referred to as inflation. If the project involves purchasing materials or supplies subject to inflation, it can impact the CPI. For instance, if the project budget includes the purchase of steel at a specific price and the price of steel increases due to inflation, it will impact the CPI.
Changes in Project Resources
Any changes to the project resources, such as the addition or removal of team members, can impact the CPI. For example, if a project requires hiring additional team members to complete the work, it will increase the project's cost and impact the CPI.
What are the Uses of CPI in Project Management?
Following are some common uses of the Cost Performance Index (CPI) in project management:
Tracking Project Progress
The CPI is typically calculated and tracked regularly throughout the project to ensure that the project is on track and within budget. By tracking the CPI, project managers can identify potential cost overruns early on and take action to bring the project right back on track.
Evaluating Project Performance
The CPI is often used in conjunction with other project metrics, such as the schedule performance index (SPI), schedule variance (SV), and cost variance (CV) to evaluate the project's overall performance.
A high CPI combined with a high SPI may indicate that the project is progressing well, while a low CPI combined with low SPI may indicate that the project is experiencing problems.
Identifying Cost Overruns
If the CPI indicates that the project is running over budget, it can be used to identify the cause of the cost overrun and take corrective action to bring the project back on track.
Negotiating with Stakeholders
Suppose the CPI indicates that the project is running over budget. In that case, it can be used as evidence to negotiate with stakeholders and secure additional resources or funding to complete the project.
Determining Project Profitability
The CPI is often used to determine the profitability of a project. A high CPI indicates that the project is running efficiently and will likely be profitable. In contrast, a low CPI may indicate that the project is running inefficiently and may not be profitable.
How to Improve the CPI of a Project?
It is essential for project managers to closely monitor the CPI and take action to address any issues that may be causing a negative impact on the metric. This can include revising the project plan, adjusting the budget, or implementing cost-saving measures.
Besides these things, the project manager can improve CPI by using other metrics in conjunction with the Cost Performance Index. Using CPI in isolation to evaluate the cost efficiency of a project can give you a better picture of the project's performance.
The other metrics that should be used with CPI include the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) and Cost Variance (CV).
The SPI measures the efficiency of the project schedule, while the CV measures the difference between the budgeted cost and the actual cost. The project managers should use other metrics to get a more comprehensive view of project performance.
In addition to the Schedule Performance Index and Cost Variance, project managers should also use Earned Value Management (EVM) to improve the CPI of a project. By using both in conjunction, the project managers can track the progress of a project by simply comparing the earned value of the project to the planned value. Here, the earned value is the value of the work completed, while the planned value is the budgeted cost for the work. By comparing these two values, project managers can identify any discrepancies and take action to address them. Besides using other metrics, the project manager can improve the CPI by carefully managing the project scope. This includes identifying and managing any scope changes and ensuring that the project scope aligns with the project objectives and budget.
Final Thoughts on Cost Performance Index (CPI)
Understanding and effectively utilizing the Cost Performance Index (CPI) is vital for project success. CPI provides a clear metric for evaluating project efficiency, identifying cost overruns, and ensuring financial performance aligns with project goals. By regularly monitoring and analyzing CPI, project managers can make informed decisions, negotiate with stakeholders, and implement strategies to improve cost performance.


