Free Float vs. Total Float: Understanding Project Scheduling Concepts
Published:
Updated:
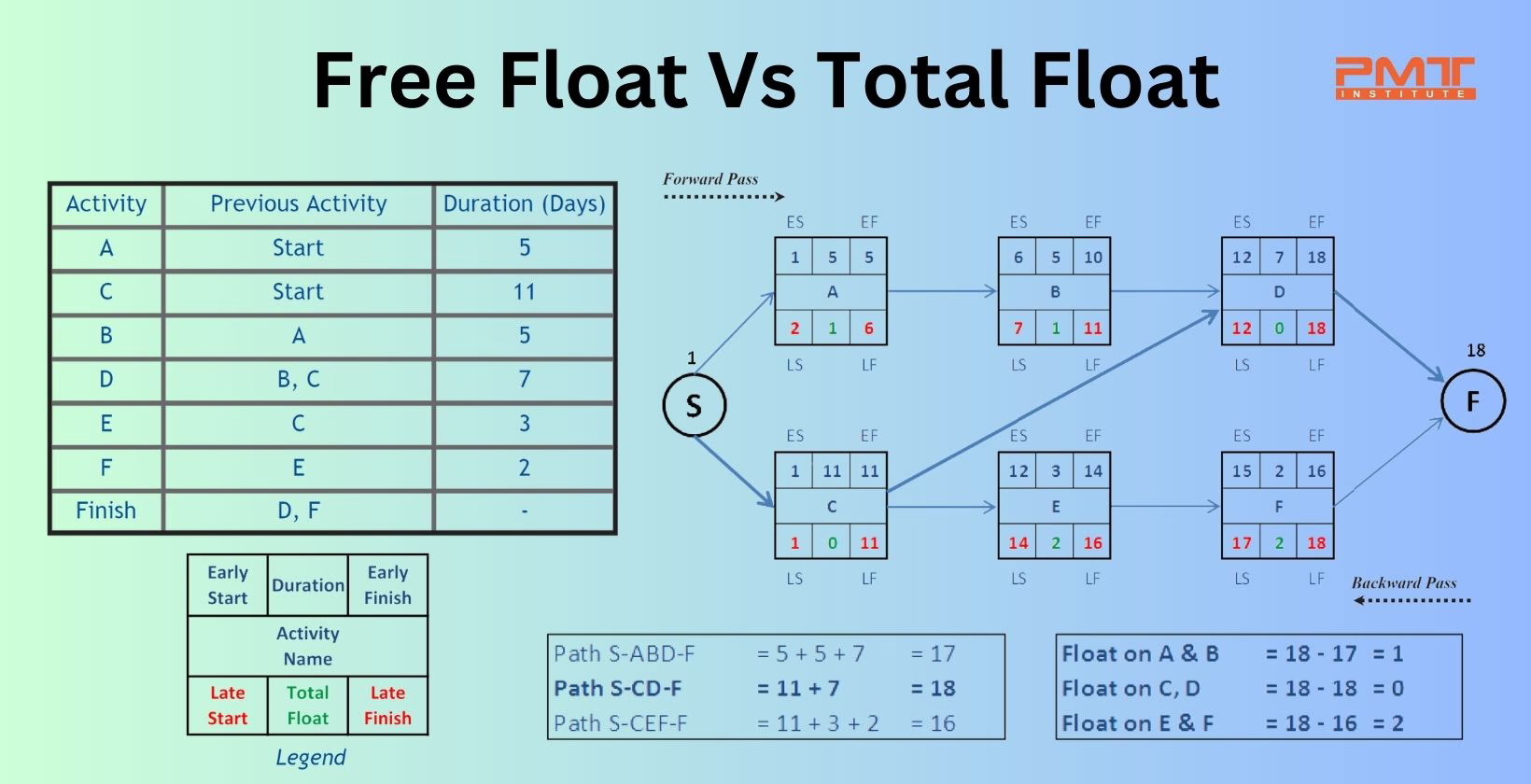
The term "float" in project management means the flexibility in the project's timeline that permits the operation to be delayed. Until Project Managers have complete control over the time, they can employ “float” in project timelines to better regulate how activity length affects the finish date. The two main forms of float are free float and total float. Total float and free float pertain to the measure of time, or planning flexibility, connected with ongoing projects. Float can be experienced when two or more operations are taking place simultaneously.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Free Float: Explanation of free float, including its formula and application in project management.
- Total Float: Understanding total float, its calculation, and its role in project scheduling.
- Comparison: Key differences between free float and total float, and their respective impacts on project planning.
- Critical Path Method: Overview of the Critical Path Method and its advantages in managing project schedules.
- Practical Examples: Illustrative examples to help understand the concepts of free float and total float.
Free Float
Free float is calculated by deducting the activity's early completion (EF) from the subsequent activity's premature start (ES). It can also be defined as the time period that a scheduled operation may be postponed without postponing the premature start time of any subsequent successor activity along the network path. Only the final activity in a series is used to compute free float.
Formula
Free Float = ES (of successor) - EF (of current).
How to Calculate Free Float ?
You can calculate free float by using the following formula:
Free Float=ES next task - EF (current task)
- ES: Early Start of the next task
- EF: Early Finish of the current task
Free float represents the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the start of the next task in the sequence.
Total Float
The difference between the early start time (ES) and the late end time (LS) is defined as the total float. The total float is distributed among the actions in a sequence which can be described as the events that occur among a location of path bifurcation and a position of path convergence.
Therefore, the total float can also be described as "slack" or "float," which defines the length of time a task may be postponed given that it does not affect the entire project's timeline.
Formula
Total Float or Float = LS - ES or LF - EF
How to Calculate Total Float ?
To calculate total float, use the following formula:
Total Float = LS - ES or LF - EF
- ES: Early Start of the next task
- EF: Early Finish of the current task
- LS: Late Start
- LF: Late Finish
Total float represents the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the project completion date.
Example 1:
If an activity or operation 1.2 has a timeline of 4 days and is occurring concurrently with activity 1.3, which has a timeline of 8 days, this means activity 1.2 has a total float of 4 days. In other words, if it is postponed for up to four days, it will have no effect on the project or its deadline.
Example 2:
Another example is to show the difference between total float and free float.
Imagine a project with three tasks: A, B, and C.
Task A is to lay the foundation for a building and has a duration of 10 days.
Task B is to construct the walls and has a duration of 20 days. It can only start once task A is completed.
Task C is to install the roof and has a duration of 15 days. It can only start once task B is completed.
In this example, the total float of different tasks is as follows.
-
The total float for task A is ten days since it can be delayed by up to 10 days without delaying the completion of the whole project.
-
The total float for task B is 15 days since it can be delayed by up to 15 days without delaying the completion of the whole project.
-
The total float for task C is five days since it can be delayed by up to 5 days without delaying the completion of the whole project.
The free float of different tasks in the project is mentioned below
-
The free float for task A is ten days since it can be delayed by up to 10 days without delaying the start of task B.
-
The free float for task B is 0 days since it can only be delayed by delaying the start of task C.
-
The free float for task C is not applicable, as it is the last task in the project.
As you can see, a task's total and free float can be different. Free float is a measure of a task's flexibility and how much it can be delayed without affecting other tasks. In contrast, the total float is a measure of a task's flexibility and how much it can be delayed without affecting the overall completion date of the project.
Comparison between Free float and Total float
-
Free float can be a negative value, while total float can never be a negative value.
-
Free float refers to individual activities, while total float refers to the project.
Importance of Understanding Total Float and Free Float
For project managers, it is important to be able to understand and differentiate between Total float and free float. A few reasons are listed below:
Tracking Progress
The most important factor for project management is tracking progress. Understanding total and free float allows you to establish whether or not the project is on the right track. If the float is large, it gives the project managers a high probability that the project will finish on time.
Time Optimization by Priority
It allows project managers to choose which activities are high priority and which are at low priority. This improves time optimization as well.
An Excellent Resource
Since it is excess time in the project, it can be utilized by project managers to address unanticipated challenges or upcoming risks. Once they know how much float they have, they can use it efficiently to their benefit and the project.
Critical Path Method
Free float and Total float are a part of the critical path method. Therefore, we need to understand the concept in detail. The critical path method is a strategy for identifying activities required for the execution of the project and determining schedule flexibility.
In project planning, a critical route is the longest series of operations that must be completed on schedule for the project to finish. Any disruptions in important activities will cause the remainder of the activities to be delayed. It mainly focuses on identifying the timeline of the whole project, the timeline of specific activities, and task dependencies.
Advantages of the Critical Path Method
-
The critical path method can be used to contrast predictions with a substantial performance that enhances the planning process. Information from the current project can be utilized to guide upcoming project plans.
-
It improves resource management because project managers can prioritize tasks, giving them a better notion of how and where to deploy resources.
-
It helps avoid setbacks that result in wasted time. CPM uses a network diagram to plot out the project's requirements and dependencies, and it paints a picture of which tasks can be carried out simultaneously and which cannot, allowing project managers to plan efficiently.
Summary
In conclusion, the critical path method's main float types are free float and total float. Project managers use them to control the time of a project. They employ "float" in the project schedules and, in this way, better regulate how each activity timeline affects the project's overall timeline. While total float refers to how far an operation may be postponed while not impacting the project's completion schedule, free float refers to how far an operation can be pushed without influencing its subsequent activities. Both are crucial to saving time while increasing the efficiency of the overall project.


