CPI vs. SPI in Project Management: Key Differences and Applications
Published:
Updated:
Whether you're working as a project management professional or studying for your project management professional exam, it is important for you to understand the two key metrics that are often used in project management; Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI).
While both metrics sound similar, they are calculated differently and provide different insights into the progress and performance of a project. This is why it is essential to understand the difference between them in order to analyze any project.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- CPI Definition: Cost Performance Index (CPI) is calculated as Earned Value (EV) divided by Actual Cost (AC), indicating cost efficiency.
- SPI Definition: Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is calculated as Earned Value (EV) divided by Planned Value (PV), indicating schedule adherence.
- Key Differences: CPI focuses on cost management, while SPI focuses on schedule management, both critical for project success.
- Applications: Understanding and applying CPI and SPI helps better track, manage, and control project performance.
What is the Cost Performance Index?
CPI, or Cost Performance Index, is a measure of calculating the cost efficiency of any project. It is the ratio between the budgeted cost and the actual cost of the project. CPI is used to find out whether the project will be completed within the budget or not. In order to calculate CPI, you need to divide the Actual Cost of a project by the Earned Value. The formula for calculating the CPI is
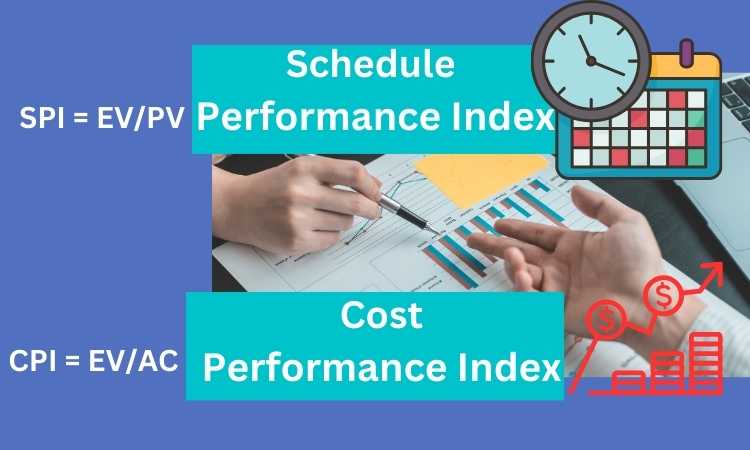
CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
Assume that you're a project manager and you're working on a project that has a budget of $100,000. After 6 months, the budget spent on the project is $60,000 and only 40% of the work is completed.
Actual Cost = $60,000
Earned Value = 40% of $100,000 = $40,000
The CPI of the project would be (40,000/ 60,000 = 0.66).
This ratio of less than 1 indicates that the project is over budget. If the CPI is greater than 1, it indicates that the project is under budget. While CPI = 1 means the project is within the budget.
What is the Schedule Performance Index?
SPI, or Schedule Performance Index, is a metric for measuring the efficiency of the project concerning the time or schedule of the project. Basically, it is used to figure out whether the project will be completed ahead, behind or on schedule.
It is calculated by dividing the planned value of the project by the earned value. The formula for SPI is
SPI = Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV)
Let's say your project has a planned value of $100,000 and an earned value of $80,000. According to this example, the SPI of the project will be 0.8.
SPI = 80,000 /100,000 = 0.8
This ratio indicates that the project is behind schedule as the SPI of the project is less than 1. If SPI is greater than 1, the project will be ahead of the schedule. While an SPI equal to 1 indicates that the project will be completed within the planned time.
Cost Performance Index Vs. Schedule Performance Index
CPI (Cost Performance Index) and SPI (Schedule Performance Index) are key metrics in earned value management:
- CPI measures cost efficiency: CPI = EV / AC
- EV: Earned Value
- AC: Actual Cost
- CPI > 1: Under budget
- CPI < 1: Over budget
-
SPI measures schedule efficiency: SPI = EV / PV
- EV: Earned Value
- PV: Planned Value
- SPI > 1: Ahead of schedule
- SPI < 1: Behind schedule
These indices help in assessing project performance and making informed decisions.
Cost Performance Index and Schedule Performance Index Comparison Table
To better understand the key differences and applications of the Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI), refer to the comparison table below:
| Criteria | Cost Performance Index (CPI) | Schedule Performance Index (SPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | CPI = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC) | SPI = Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV) |
| Purpose | Measures cost efficiency of project work | Measures schedule efficiency of project work |
| Ideal Value | CPI = 1 (On Budget) | SPI = 1 (On Schedule) |
| Interpretation | CPI > 1 (Under Budget) CPI < 1 (Over Budget) |
SPI > 1 (Ahead of Schedule) SPI < 1 (Behind Schedule) |
| Usage | Helps in cost control and budget forecasting | Helps in schedule control and timeline forecasting |
| Impact on Project | Directly affects project budget management | Directly affects project timeline management |
| Common Application | Budget performance analysis and adjustments | Schedule performance analysis and adjustments |
| Relation to Earned Value (EV) | Compares EV to actual expenditure | Compares EV to planned expenditure |
| Key Metric in | Cost management processes | Schedule management processes |
This table highlights how CPI and SPI are used to gauge different aspects of project performance, providing valuable insights into both budget and schedule management.
One key difference between CPI and SPI is the way that they are calculated. CPI is calculated using the actual cost of a project and the earned value, while SPI is calculated using the planned value of the project and the earned value.
Another key difference between CPI and SPI is the way they are used. CPI is often used as a benchmark for cost management which allows project managers to identify areas where cost savings can be made.
On the other hand, SPI is used as a predictor of future performance, as it provides a way to forecast how the project is likely to progress based on its current schedule. To sum it up, CPI and SPI are the two key metrics that measure different aspects of a project's progress and performance. However, they are equally important for any project manager as they help them to track the progress of the project and help in making informed decisions about their projects.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
Overview of EVM
EVM (Earned Value Management) utilizes scope, time, and cost parameters to assess project progress and performance. It provides a quantitative analysis of a project's actual performance compared to its planned performance.
Role of CPI and SPI in EVM
CPI and SPI are critical metrics within EVM. SPI measures schedule efficiency by comparing earned value to planned value, while CPI measures cost efficiency by comparing earned value to actual costs. Together, they offer a comprehensive view of project health, aiding in decision-making and corrective actions.
Schedule Variance
Understanding Schedule Variance
Schedule Variance (SV) indicates the difference between the work actually performed and the work planned. It is calculated as SV = Earned Value (EV) - Planned Value (PV). A positive SV indicates a project is ahead of schedule, while a negative SV indicates a project is behind schedule.
Using SPI to Measure Variance
SPI is used to measure schedule variance effectively. An SPI greater than 1 signifies that the project is progressing ahead of schedule, while an SPI less than 1 signifies a delay. This helps project managers make informed decisions to align the project with its timeline.
Cost Variance
Understanding Cost Variance
Cost Variance (CV) indicates the difference between the budgeted cost of work performed and the actual cost. It is calculated as CV = Earned Value (EV) - Actual Cost (AC). If the CV is positive, then the project is under budget, while if it is negative, then the project has overrun.
Using CPI to Measure Variance
CPI is a vital tool for measuring cost variance. A CPI greater than 1 suggests cost efficiency and that the project is under budget. Conversely, a CPI less than 1 indicates cost inefficiency and that the project is over budget.
Final Thoughts on CPI and SPI
CPI and SPI are essential metrics in project management, providing insights into cost and schedule performance. Monitor these indices regularly to ensure timely and budget-friendly project completion. Using CPI and SPI principles as part of EVM leads to better project outcomes and increased stakeholder satisfaction.


