Procurement Management: Definition, Importance, Functions, Process, Benefits and How It Works
Published:
Updated:

Procurement management is a procedure in charge of supervising and managing all techniques employed to acquire the supplies, commodities, and activities necessary for efficient operations. Procurement administration is deemed significant in most businesses as it allows cutting of expenses while increasing business efficiency. It gives establishments access to vital seller and product data and guarantees the openness of the entire purchase request appeal procedure, from the first appeal to the final payment. It directly affects both the tactical business operations and the fundamental outcome of a firm as a result.
Key Takeaways
- Procurement Basics: Clear definition and explanation of procurement management and its critical importance in project success.
- Functions and Process: Detailed look at the key functions and steps involved in procurement management, from requisition to invoice approval.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Overview of key personnel involved in procurement, including procurement managers, specialists, and analysts.
- Benefits and Improvements: Understand the benefits of effective procurement management and tips on how to improve procurement processes.
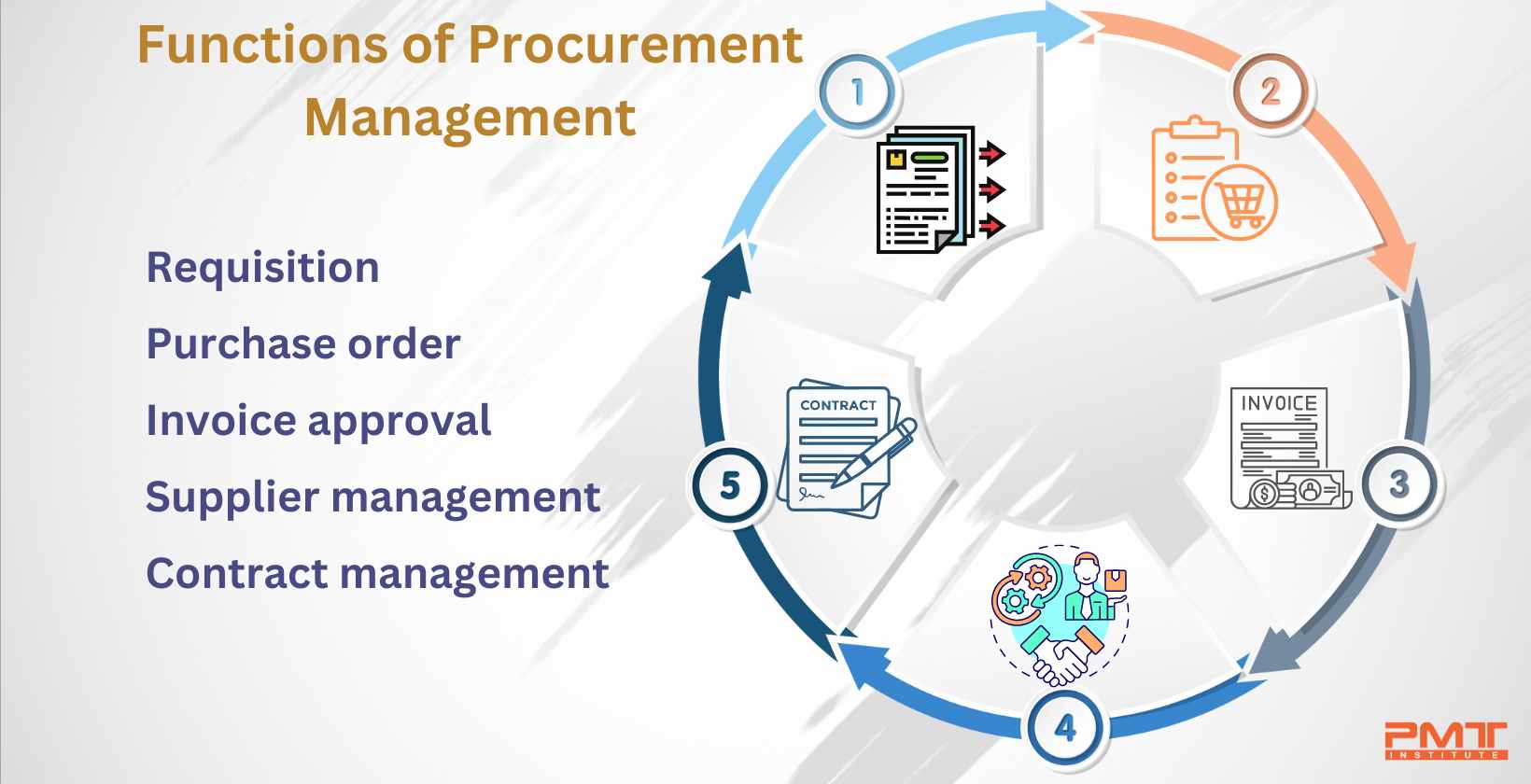
There are five overall functions which comprise the procurement management. These functions consist of purchase requests, purchase orders, invoice approval, vendor management, and contract management. A purchase requisition is a written appeal sent to the procurement section to patronize a particular item or service. It is later called a purchase order once it is sent to the vendor or supplier, comprising the tracking number, the name of goods to be bought, and the needed quantity. The invoice approval is used after the PO is affirmed. It ensures that the appropriate items and services are ordered. Furthermore, vendor management is utilized to help find suppliers, keep an eye on and track vendor efficiency, acquire quotations, discuss agreements and deadlines, and send remunerations. Contract management is performed to oversee and manage agreements.
Procurement management works successfully when a viable procurement technique is established. Such a technique guides the entire procurement team on how to effectively acquire items or services from various sellers. It takes a healthy relationship with several vendors in order to lay a budget-friendly, well-organized procurement plan out.
The process that is normally involved in the procurement management includes planning and identifying what to purchase, picking the best suppliers, contract negotiations, placing the first purchase order, increasing order, receipt and purchase evaluation, paying the invoice and remuneration.
There are benefits from performing project management. Some of these benefits include improved efficiency and accuracy, proper cost management, and lesser threat. Procurement management aids in developing and arranging specific agreements which promote confidence in the caliber of purchased goods and services. Proper cost handling is achieved through the utilization of procurement management by establishing procurement pricing and regulating additional charges associated with procurement. Any potential procurement threats are decreased with transparency in terms of sellers, contract specifications, and the quality of the goods and services procured.
What is Procurement Management?
Procurement management is alternatively coined as the source-to-settle process. It comprises certain tasks that are associated with the procurement method, such as assessment, selection, and development of official contracts. It also covers ensuring continued supplier relationships for the business. Procurement management is a part of the procurement management process, which interfaces with accounts payable to complete the source-to-settle cycle by supplying additional documentation to aid in the preparation of vendor invoices for reimbursement.
The phrase "procurement" basically refers to all of the actions taken to acquire the goods and services of a business in a certain establishment, which it normally requires supporting its everyday operations. Businesses normally encounter operations such as sourcing, negotiating terms, purchasing goods, obtaining and examining items when appropriate, and maintaining records of each stage in the procedure. Procurement is essential for understanding supply chains because it enables businesses to identify dependable vendors who are capable of delivering high-quality products at prices that are reasonable for their market.
Procurement management ensures that projects and procedures move forward smoothly and efficiently by making sure that all supplies, products, goods, and services are bought in the right way. Businesses earn a favorable influence on the foundational and strategic business operations as a result.
What is the Importance of Procurement Management?
The importance of procurement management plays a valuable role in the success of resources acquisition. Procurement management is undeniably essential because it gives firms a competitive edge over competitors by reducing costs, preventing mistakes and interruptions, and utilizing resources to the fullest. It is the primary essence of handling procurement properly.
Some other significance of procurement management is being able to minimize communication breakdowns and guarantee business success. It aids in managing connections with outside vendors and guarantees adherence to rules and conditions of contracts. Firms are able to accomplish project objectives, successfully make contract deals, and handle supply chain logistics with the help of procurement management. It facilitates the arrangement of profitable manufacturing and supplier agreements, as well as drives the development of innovative procedures. Procurement management is crucial to growing commercial operations. It leads corporate social responsibility and diversity initiatives by proactively collaborating with various vendors in the marketplace.
A lot of businesses ask about, "what is procurement?". Procurement is an activity involving a purchaser and a vendor where a certain amount of supplies or services are being acquired in exchange for financial assets or funds. It technically pertains to all the activity associated with product purchases or necessary services that are essential to a company's operational tasks.
Other firms describe procurement as all the steps, from collecting business needs and locating vendors to monitoring the receipt of goods and adjusting remuneration conditions. Some businesses, on the other hand, view procurement as a more limited variety of duties, such as issuing purchase orders and making payments.
What are the Functions of Procurement Management?
Procurement management is tagged as the act of procuring goods, services, or works from an outside supplier. It is essential to an organization's success as it guarantees the prompt provision of excellent products and services at an affordable price, while mitigating risks and optimizing money's worth. A lot of firms are able to keep a competitive edge and accomplish their strategic objectives with the aid of effective procurement management. Procurement management is associated with functions that help businesses align their corporate goals with their acquired resources and business funding.
Listed below are some of the functions of procurement management:
-
Requisition: One of the functions of procurement management is the purchase requisition, better known as a requisition. Preparing a purchase requisition commences a firm's purchasing journey. A purchase requisition is an expressed demand from an employee or department to patronize certain products or services necessary for business operations.
-
Purchase order: The purchase order serves as the basis for the purchaser and vendor's contract. It is a binding legal instrument created by a buyer and sent to a seller. A purchase order is essentially a list of the things to buy, similar to one's "cart" on an online store.
-
Invoice approval: It is an activity that involves examining and confirming vendor invoices prior to paying the cost. The approval process for the invoices begins when the buyer receives a supplier invoice, either by email, post, or other mediums. The invoice is then categorized and sent to the correct point person for approval.
-
Supplier management: Supplier management is another crucial function of procurement management. Evaluating the performance of suppliers, identifying and establishing delivery and product standards, and sustaining connections are all parts of supplier management. Its objective is to guarantee that suppliers satisfy or surpass the buyer's standards of quality, timeliness, and price.
-
Contract management: The method for handling agreement generation, implementation, and assessment is known as contract management. The goal of contract management is to increase an organization's operational and financial performance while lowering financial distress. Companies are under ever-growing pressure to save costs while boosting productivity.
1. Requisition.
Requisition is the primary function in procurement management. It is basically an appeal to patronize certain goods and apply services that a firm needs for its operations. A requisition is sometimes tagged as a purchase requisition. The requisition is either direct or indirect spending in accordance with the specifications of the needed materials.
Purchase requisition is important for procurement management because every purchase, numerous or few, expensive or cheap, starts with a requisition. It initiates procurement, controls expenditures, guards against fraud, and provides crucial records for accounting audits. Budgeting and planning, interaction, records management, conformity, and visibility are a few of its major purposes. Purchase requisition enables companies to be certain that their purchasing actions are well-organized, budgeted, legal, and clear.
A petition for a purchase is normally created by a certain employee, for smaller firms, or a particular department, for bigger corporations. It is then submitted to the procurement team responsible for processing such appeals. The procurement department is permitted to carry out market research to find potential vendors, get estimates, and bargain deals. The requisition is usually approved by a higher authority in the procurement team or senior management. They are accountable for examining the requisition and confirming that the desired items or services are required, the funding is adequate, and the procurement process complies with the company's rules and regulations.
2. Purchase Order.
Another crucial function of procurement management is the purchase order. It is a binding legal instrument between the buyer and the seller composed of pertinent details about the product or services being demanded. These details primarily include a tracking number for the request, the name of the product, the quantity of items needed, and other supplementary data. Small firms that place bulk orders for items typically use purchase orders.
Purchase orders are essential to procurement management because they serve as the basis for the purchaser and vendor's contract. A purchase order provides the supplier with protection from non-payment because the order is fulfilled before the consumer receives their bill. The customer agrees to buy the specified items or services for the specified price by placing an order, getting rid of unnecessary and unauthorized purchases.
The purchase order is normally issued by the procurement department, which is in accordance with the details included in the requisition, such as the specifications, quantities, and delivery dates of the items or services being acquired. The purchase order is created following the approval of the purchase requisition. The same people process the purchase order, which entails confirming the information's validity and ensuring that the PO complies with the company's standards and procedures. The purchase order's terms and conditions, such as the cost, delivery schedule, and mode of payment, are negotiated as well by the procurement department with the seller. The purchase order is affirmed by a responsible approving authority, normally a procurement committee or a senior manager, where the PO's accuracy and the procurement process's adherence to the organization's regulations must be confirmed.
3. Invoice Approval.
Invoice approval is a procedure that comprises examining and accepting supplier bills prior to actually recording them as costs. An invoice is simply a piece of form indicating the cost of the supplies being demanded from a certain company. It includes the name of the items ordered and their quantity.
The approval of invoices is a vital stage in procurement administration as it guarantees that the business pays for products and services that have been delivered and that adhere to the conditions of the agreement or purchase order. The accounts payable process's crucial phase of invoice validation helps businesses assure correctness.
Invoice approval normally starts upon the receipt of an invoice from a supplier, which is typically sent through email, post, and other convenient platforms. The supplier's invoice is sent to the accounting department. They are the ones who are obliged to process invoice approvals. The invoice approval process typically involves developing another invoice as company reference where all pertinent data must be gathered or manually input into the organization's invoice approval loop. A purchase order matching is later conducted to locate and connect other relevant purchase documents, such as purchase requisitions, order receipts, and other documents. The exclusions have to be subsequently to pinpoint mismatch or lacking details. The invoice is routed to appropriate approvers once it is checked. It is sent to the accounts departments for payment if the invoice is approved.
4. Supplier Management.
Supplier management is a crucial function in procurement management. It is a procedure which revolves around sellers and vendors. Supplier management involves the assessment of supplier performance, recognition and establishment of delivery and quality standards, and maintenance of relevant connections.
The significance of supplier management comes in many crucial areas. Some of these indicate that supplier administration promotes better product and service delivery, lower costs, and builds stronger supplier connections. Additionally, purchasers are able to lower the likelihood of interruptions to their own operations by regulating the performance of suppliers.
The procurement or sourcing department is the one responsible for identifying potential suppliers, sending proposals of request, arranging agreements, and picking the most suitable ones for the business. It is anticipated that the processing of supplier management is facilitated by a number of departments or point persons. Some of the most common departments involved in the supplier management are the finance department, quality assurance section, legal department, and production department. It is to assure that the supplier being considered has a set of business objectives and products that are in line with the company's fundings, quality standards, terms and conditions, delivery specifications. It is the senior management or executive team who makes the final decision and approves supplier contracts.
5. Contract Management
Contract management is another crucial function in the procurement procedure. It is the process of handling contract development, implementation, and assessment to improve an organization's operating and financial outcomes while lowering risks. The need for a reliable and automated platform for managing contracts is facilitated by the fact that contract administration tends to be a particularly time-consuming element of a company.
Contract management aids businesses in managing their interactions with partners, clients, suppliers, and staff. It entails all phases of contract formulation, arrangement, implementation, and oversight. Contract management is considered crucial for several reasons, including risk mitigation, cost savings and efficiency, performance monitoring, compliance, healthier relationships between parties, conflict resolution, and strategic decision-making.
Contract management is initiated in the contract department, where specific needs, rules, and restrictions of the agreement are specified. Such tasks are usually carried out by the sales force, legal team, or procurement department. It is the contract manager who leads the processing of contracts once they are created. These experts are in charge of managing the entire contract duration, from creation to termination. They closely collaborate with all parties involved, such as legal teams and other relevant business partners, to ensure that agreements are carefully carried out and that they satisfy the requirements of every client. Contract managers can be either internal staff members or outside advisors.
How Does Procurement Management Work?
Procurement management works by initially crafting a sensible procurement strategy that is in accordance with the policies and procedures of a particular establishment. The procurement team must be able to build a healthy and transparent connection with team members, clients, and senior management to ensure a well-organized implementation of the procurement journey. Building strong relationships within the business promotes a smooth procurement procedure without compromising quality and timeliness.
Procurement teams are typically tasked with performing the following duties, namely: locating vendors, monitoring orders, increasing supplier variety, and setting forth contract terms and expenses. Additionally, they need to look for opportunities to expand the supplier options, establish a list of recommended vendors for upcoming requirements, and ensure that everyone complies with their duties. The procurement materials involved in the process include raw materials, components and sub-assemblies, finished goods, indirect materials, services, capital goods, Maintenance, Repair, and Operations supplies, and office supplies.
There are various ways to facilitate the procurement of resources that are going to be used in a particular company or business, such as office equipment. The following are provided to briefly state the purchasing methods of office equipment, namely: a direct purchase from the vendor, an order from manufacturers' reps, a tender, leases and rentals, buying on public marketplaces, a public auction, the internet, or a website.
A direct order is done when an order is made for the delivery of the equipment provided that the company is pleased with the quote and the items' condition. Ordering from a representative is attained through a technical specialist who supports the equipment marketing or a commission agent who works with the manufacturer's representatives and helps in placing an order for efficient equipment. A tender, on the other hand, is an order to contractors to submit favorable bids for the supply of commodities. Renting and leasing are appropriate when the office lacks the financial resources to complete an upfront payment. Patronizing from the public market gives assurance that there is no time lost in procurement while providing a range of machines from which to choose.
Furthermore, auctions are preferred options when a business wants to buy second-hand office supplies or machinery that costs lower than brand new equipment. Ordering workplace equipment online is a contemporary method where the website provides details on the device and the delivery schedule. It provides ease for online payments as well.
What are the Steps of a Procurement Management Process?
The procurement management process pertains to the procedure employed when handling distinct sorts of purchases in businesses and firms effectively. It is a crucial element of any firm's supply administration, held accountable for the strategic sourcing of products and services that satisfy the demands of the firm. The procurement administration is a detailed process designed to guarantee that the business gets the best goods and services at the most affordable prices.
It is essential to follow the step-by-step process in the procurement procedure to uphold equality, encourage transparency, and ensure compliance with the law. Following the steps rigorously allows better resource management, risk mitigation, effective resource management, quality control, and transparent client interaction. Better decision-making is encouraged by a strongly outlined procurement method since it guarantees that all pertinent data is taken into account and assessed. Companies can accurately evaluate the standard of the goods and services supplied by vendors by following an organized process, ensuring that they adhere to the necessary regulations and standards. A structured procedure guarantees quality control and permits performance evaluation, resulting in ongoing improvement and better financial value.
A lot of people are asking, "what is a procurement process?" A procurement process pertains to the step-by-step procedure that a person or team needs to take whenever purchasing a product or paying for a corporate service. It is a collection of techniques used to improve a firm's procurement activity while achieving expected outcomes that are cost-saving, time-bound, and of high standard.
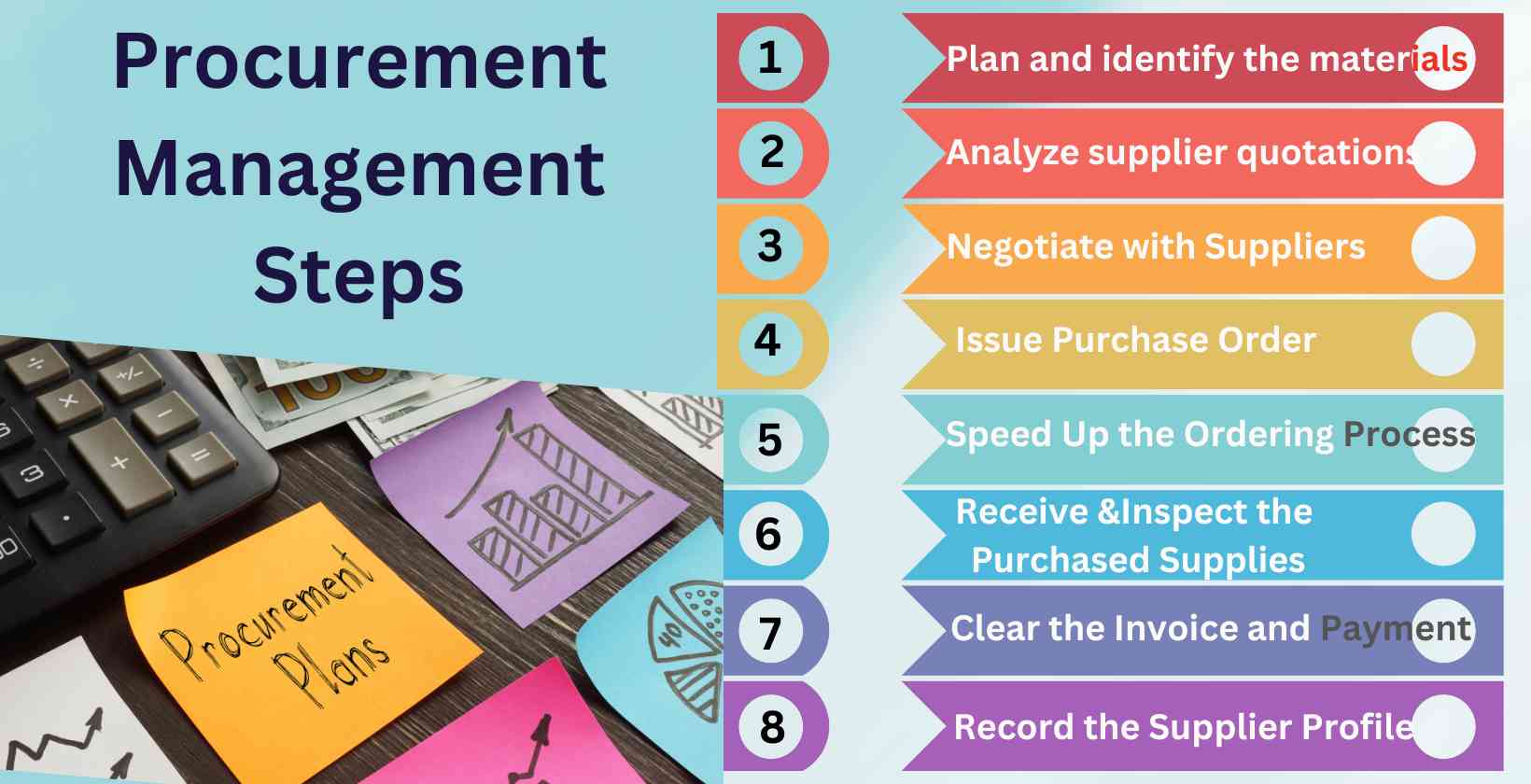
Listed below are the steps on how to conduct a procurement management process.
-
Plan and identify the materials: It is the first phase in the procurement procedure, which involves identifying the materials or equipment needed and their specifications. Planning and identifying materials must be in accordance with a company's existing purchasing information and expectations, such as how the materials are ordered and when they are purchased or re-purchased.
-
Analyze supplier quotations: The procurement personnel or team must be able to assess the quote crafted by their suppliers. It is a crucial part of the procurement process that ensures the materials are ordered at a reasonable price, abiding by the conditions set by both parties.
-
Negotiate with suppliers: It is the third step in the procurement procedure where a company's procurement team or personnel conveys their specifications and expectations regarding the items being purchased. The deal is completed and signed once all the conditions have been agreed upon.
-
Issue purchase order: A purchase order is issued once the agreement between the supplier and buyer is sealed. It is a written demand for specific equipment or materials that indicates the product details, terms and conditions, exact pricing, and quantity.
-
Speed up the ordering process: Speeding up the ordering process means having the items delivered before the specified date and time. It is to test the suppliers' flexibility and determine the timeliness of their deliveries.
-
Receive and inspect the purchased supplies: It is the stage in the procurement procedure where the materials are already delivered and are subjected to quality checking. The procurement team is tasked with ensuring that the contents in the purchase order are in line with the invoice and the materials being delivered.
-
Clear the invoice and payment: It is the last step to complete the Procurement Management Process. The procurement team must match the purchasing document to the accounts payable to determine an accurate overall cost. The payment is made once the invoice and the payables coincide.
-
Record the supplier profile: Supplier profiles must be kept and properly documented for corporate purposes such as tax and audit and continued connection with them. It is important to create a good relationship with suppliers to conveniently facilitate product warranty and upcoming reorders.
1. Plan and Identify the Materials.
The first step to take in the procurement management process is to plan and identify the materials needed. It involves designing the procurement techniques to obtain essential goods and services, detailing the required products and services, and specifying the product specifications. The procedure entails figuring out the necessary materials' requirements in terms of quantity, durability, standards, and delivery dates.
Planning and material selection are essential because they establish the groundwork for a fruitful procurement procedure. By carefully analyzing the project's specifications, businesses can reduce risk factors associated with inadequate planning, such as budget overruns, disruptions, and other dangers. Having a clear grasp of the required materials enables companies to streamline procurement, make well-informed decisions, and ensure a smooth project execution.
The identification and planning of supplies is a necessary step in order to proceed to the subsequent phase in the procurement procedure, which pertains to supplier quotations. The procurement team or personnel must choose the best sourcing strategy, such as direct purchase, open bidding, or negotiation. By selecting the appropriate method, companies can improve value for money, cut expenses, and ensure the prompt delivery of goods and services. It also aids in selecting the best suppliers, assessing their capacities, and forging long-term connections to guarantee ongoing supply and assistance.
Some of the prerequisites for planning and identifying materials are the following: well-defined project goals, funding and cost analysis, and specification definition. Clear project goals, constraints, and scope must be stated to establish a reliable foundation for procurement planning. The procurement team needs to create a realistic budget for the procurement process and calculate the cost of supplies, taking market volatility, delivery costs, and transportation costs into consideration. They must also define the technical requirements, quality standards, and performance standards for the products and services being purchased, aiding in the identification of suitable sellers and products.
2. Analyze Suppliers' Quotations.
The subsequent step involved in the procurement management process is to analyze the suppliers' quotations. It is usually done through the submission of an RFO or Request For Quotation from a certain establishment. A request for quote or RFQ is usually delivered by the purchasing team to potential suppliers to obtain a quote. The quote must be specific so that companies are able to compare several factors. It is typically the time to select the supplier with the highest quality. Evaluation of vendors must pay attention to reputation, responsiveness, reliability, and quality in addition to price.
The importance of reviewing supplier quotes comes from the ability it gives businesses to pinpoint the vendors who are capable of delivering high-quality products and services at the most affordable rates. Assessing a supplier's dependability, responsiveness, and previous performance, which are important criteria in the selection process, are all helpful elements. By studying the supplier quotations, procurement professionals are able to find suppliers who can offer the best value for money.
The next step in the procurement management process, which is negotiating with suppliers, requires a thorough analysis of supplier quotes. The data acquired during the analysis phase helps procurement specialists understand the price structure of the suppliers and identify areas where they need to negotiate for more favorable conditions.
Moreover, procurement experts need to have excellent interpersonal abilities to interact with suppliers, comprehend their offerings, and negotiate successfully. Procurement specialists should also effectively organize and use technology tools for assessing supplier quotations.
3. Negotiate with Suppliers
The procurement procedure includes the need to negotiate with suppliers. Business owners must be able to sit with their suppliers and exchange thoughts regarding the proposed prices and anticipated expenditures. Getting at least three estimates from vendors before choosing one is a frequent best practice. Procurement officers or top management must examine each quote carefully and make an effort to reach a suitable agreement. They need to make sure that viable alternatives are prepared in case there is a need to withdraw from a transaction. The procurement officer must obtain the final terms on paper as soon as an agreement has been reached.
It is crucial to negotiate with suppliers as it enables businesses to get better deals on products and services, as well as greater bargaining power. Effective negotiation establishes solid working ties with the supplier, enhancing coordination and cooperation. Negotiation with suppliers is a great strategy to cut costs, lower risk, and increase the total value of the procurement process.
The following step in the procurement management process requires negotiation with suppliers. The contract, which serves as the official agreement regulating the connection between the company and the provider, contains all the conditions agreed upon during this step. Without competent negotiation, the contract's terms and conditions may not fulfill the needs of the organization, creating conflict and even expensive legal problems.
Procurement specialists must be able to build and uphold relationships with suppliers based on trust and respect. Knowledge of market and industry trends, as well as rival suppliers, is necessary for procurement specialists. They must be able to analyze data and apply technological tools to effectively support their negotiations.
4. Issue Purchase Order
Procurement facilitators need to issue purchase orders subsequently. It is one of the most significant points in the procurement process because a purchase is not completed in the absence of a purchase order. Releasing a purchase order typically occurs when a PO is created by the procurement personnel and delivered to the vendor. The PO needs to be specific enough to specify the precise services or items required and to make it attainable for the provider to satisfy the request.
A purchase order is crucial because it serves as the transaction's formal record, guaranteeing that the provider and the corporation are both aware of their respective responsibilities. The purchase order consequently acts as a document of reference that the business utilizes to verify if the supplier provided the items or services that abide by the agreement being consented to.
The issuance of a purchase order is an activity that is vital for the subsequent phase of the procurement administration process. A corporation is able to prove that it has obtained the requested services or merchandise through the purchase order, which acts as an assessment of the merchandise to be dispatched.
There are a few necessities that must be met to properly release a purchase order. These include the ability to construct a detailed purchase order with all relevant data, knowledge of the costing and transport details of the providers, and an adequate grasp of the corporation's procurement standards. Procurement specialists must be able to communicate efficiently with providers to guarantee that they have a clear perspective of the points and specifications of the purchase order. Additionally, procurement specialists must be proficient with digital tools to successfully produce and handle purchase orders.
5. Speed Up the Ordering Process.
The procurement procedure often includes the necessity to speed up the ordering process. A product order or PO must occasionally be expedited. It is often the result of a change in the plan or prior product obsolescence. Examining how quickly deliveries are produced during the acceleration process is one technique to address such difficulties. It highlights any underlying issues, such as ambiguity around delivery deadlines, reimbursement schedules, and project accomplishment.
The benefit of accelerating the ordering process is that it makes businesses more adaptable and receptive to shifting business needs. Organizations can increase customer happiness, cut expenses, and improve operational efficiency by reducing the time it takes to order goods and services. A quicker ordering procedure makes businesses stronger competitors in the marketplace.
Certain conditions must be met in order to expedite the ordering procedure. These consist of an effective, well-documented procurement procedure recognized by all parties. Technology should be used to automate and expedite procurement procedures whenever possible, and procurement experts must have the requisite knowledge and resources to handle the procurement process effectively.
Procurement specialists must be able to analyze procurement data to pinpoint problem areas and monitor the performance of suppliers. Utilizing such data helps the firm get the best value for its money and streamline the procurement process.
6. Receive and Inspect the Purchased Supplies.
The subsequent phase in the procurement procedure is to receive and inspect the purchased supplies. Procurement officers are tasked with accepting the procured products. They are obliged to assess the receivables for quality, quantity, cost, and more. The procurement team needs to thoroughly check deliveries for any mistakes or damage and ensure that the quality of the items meets or exceeds expectations. They must ensure that everything arrived as stated in the purchase order.
Receiving and checking the purchased materials is crucial since it guarantees that the company receives the right products or service with the expected quality. Additionally, the company has the chance to identify any problems or discrepancies and quickly address them with the provider through this process. Procurement professionals can ensure that the supplier is held responsible for providing high-quality goods or services by verifying that the received goods or services satisfy the organization's needs.
The next phase in the procurement management process requires receiving and examining the purchased products. The supplier's invoice is compared to the purchase order to ensure that the products or services obtained are consistent with the invoice. It is challenging for the company to accurately reconcile the supplier's invoice without proof of receipt and inspection of the purchased materials.
There are a few requirements that must be met in order to successfully receive and inspect the supplies being ordered. These include defined protocols for receiving and inspecting goods and services, clear lines of communication between the organization and the supplier, and a well-documented procurement process that specifies the quality requirements and specifications that suppliers must meet. Procurement specialists must also have the necessary training and equipment to efficiently inspect the acquired items. This involves having a working knowledge of quality control procedures, the ability to identify flaws or anomalies, and promptly documenting and notifying any problems to the supplier.
7. Clear the Invoice and Payment.
Procurement professionals must be able to clear the invoice and payment of the products being procured. Aligning the purchase with the accounts payable is the final step to complete the procurement process. Businesses must make an effort to create a standardized accounts payable invoice payment procedure that verifies that payments match the amount of the invoice and the due date.
Clearing the invoice and remuneration is crucial because it ensures that the supplier receives fast and accurate payment for the goods or services rendered. The smooth operation of the purchasing process can be ensured by procurement professionals through clearing the invoice and making the payment on time. Having a systematic procedure ensures that bills are always paid on time, avoiding late fees and fostering positive supplier relations.
The following stage in the procurement management method, which is to wrap up the procurement procedure, requires clearing the invoice and payment. It involves ensuring that all paperwork is in order, the procurement process is fully documented, and all items or services have been acquired and paid for. Effectively wrapping up the purchasing procedure becomes quite challenging without clearing the invoice and payment.
Some of the requirements that must be met in order to effectively clear the invoice and payment include established methods for clearing invoices and processing payments, and open lines of dialogue between the company and the supplier. Additionally, a well-documented procurement process that specifies the terms and conditions for settlement is a prerequisite. Those responsible for this task must have the necessary knowledge and equipment to efficiently clear the invoice and payment. This involves understanding accounting procedures, being able to match invoices with purchase orders and receiving reports, and accurately and promptly making payments.
8. Record the Supplier Profile.
The concluding phase of the procurement method is to record the supplier profile. It is somewhat like a wrap-up for the entire purchasing procedure. It is the process of keeping accurate records for tax and audit purposes. Additionally, it verifies the product guarantee and makes it simpler to order the item again in the future. Most businesses provide the supplier statistics and feedback based on key performance factors as well, which aids in pinpointing procedure enhancement opportunities.
The documentation of the entire procurement procedure is quite essential for most companies. It involves recording the purchase requests, price negotiations, invoices, receipts, and anything else in between. These documents are helpful for a variety of purposes. Some of these benefits are that they aid in tax calculations, auditing procedures, and future orders of items at the proper price for the business. Additionally, accurate and clear records are potential tools to aid in settling any future conflicts.
The supplier profile offers a thorough perspective on the suppliers and their capabilities, which is often helpful in evaluating suppliers and making educated purchasing decisions. The supplier portfolio is utilized in monitoring supplier performance and assessing the outcomes of previous procurement efforts. It also acts as a reference for upcoming procurement activities. Moreover, it gives the purchasing group a thorough understanding of the suppliers and their skills, which is essential for making well-informed judgments.
It is critical to pre-qualify the suppliers to make sure they meet the minimal standards for conducting business with the organization before recording the supplier profile. These standards often involve elements like financial security, expertise, and references. The procurement team must collect data about the suppliers, including information on their price, delivery schedules, the goods and services provided, and company history. The supplier profile is created using such data.
The supplier profile must be comprehensive and accurate since the data will be used to assess the suppliers and make wise purchasing decisions, including specifics such as contact information, the company's address, the list of goods and services, and other credentials.
What are the Benefits of Procurement Management?
Listed below are some of the benefits of procurement management.
-
Decreased costs: One of the leading benefits of procurement administration is that expenditures are gradually lowered. Purchase orders for large quantities are issued at specific times of the year with careful planning, which is capable of reducing costs.
Representatives from the procurement department are in a stronger negotiation position when time is not of the essence. Vendors and suppliers have the edge when time is limited, closing potential opportunities to negotiate the costs. It often results in much higher costs.
-
Improved accessibility of resources: Any business becomes sustainable when the needed resources are available whenever they are needed. Businesses that place regard on proper procurement planning are most likely to have sustainable access to needed materials. Planning far ahead and concentrating on long-term objectives help purchasing teams maintain constant resource availability. However, without these precautions, supplies are potential to run low on time, necessitating expensive, unexpected purchasing plans.
-
Increased efficiency and transparency of the process: One of the important elements in business is the value of transparency, especially in the procurement section. Such transparency is crucial for problem-solving, creating advancements, and gaining a broad knowledge of the various parties, interactions, steps, and processes involved in enabling large-scale procurement for complex companies. Companies that employ well-planned procurement procedures are able to enhance general efficacy, especially when scaling or iterating is the aim.
-
Lessening supplier risk: Another benefit of procurement management is to alleviate the danger of partnering with problematic suppliers. There is always danger involved when working with external parties such as vendors or suppliers, regardless of how healthy the relationship is. These threats are often experienced in terms of financial aspects, operations, legal matters, or strategy. Strong procurement systems must have an established plan for these potential scenarios as well as frameworks for identifying and evaluating risks. Therefore, efficient procurement administration lessens the likelihood and impact of risks posed by suppliers.
-
Stronger supply resilience: Procurement management is able to boost a company's resilience in terms of supplies. Successful organizations often have strategies in place that allow them to anticipate unforeseen events, beyond just planning for and having access to resources. It entails planning for scenarios in which supply is constrained. Unforeseen scenarios associated with supplies are often inevitable despite the expectation that service not be interrupted in the context of procurement. It means that organizations that want reliable procurement procedures must change their mindset from "just-in-time" to "just-in-case". Practicing such an attitude in the event of the unexpected helps supplies and general services to continually be reliable.
-
Independence to Innovate: One of the benefits of procurement management to most companies is to have the freedom to employ new strategies and eventually improve their business performance. An organization's priorities shift when they have strong procurement management strategies. Poor procurement management encourages short-term, low-level emphasis in businesses, while high procurement management ushers long-term, high-level focus. Such a perspective provides businesses the opportunity to innovate in ways they were previously unable to.
What are the Components of Procurement Management?
Listed below are some of the components of procurement management.
-
Scheduling the project: A project scheduling activity precisely indicates a specific assignment, its start date, end date, and budget. It is conducted to properly split a chunk of work into distinct and specific tasks for various responsibilities, including those of outside contractors, suppliers, and vendors of service providers. The project schedule is typically composed of the SOW or statement of work, which is otherwise called TOR or terms of reference. It outlines the assignment that needs to be done while the contractor indicates a cost and time frame. The task structure handles the costs and timelines associated with the assignments similar to internal tasks. Project members, such as contractors, are assigned with only one task in every project to avoid the notion of being intensively supervised, resulting in unhealthy connections between them or losing the benefit of employing project management methods.
-
Supplier management: Another important component of procurement administration is the management of vendors or suppliers. Supplier management is a crucial step in the procedure. It aids in ensuring that the suppliers' work is satisfactory. Strategies for supplier control must be included in a plan that explicitly states the declaration of outcomes and sources. The owner is expected to receive frequent information about the project from the vendor, often via the project sponsor. The project sponsor appropriately updates the organizational hierarchy with the help of these details, which are thorough and contain all the required data. The procurement management plan is known to have vendor control procedures included that are then transferred to the SOW or TOR. Some of the components of the supplier management plan include the metric of product quality, such as size, shape, or the caliber of delivered widgets, site examinations, evaluations of infrastructures used for external production, and periodic project meetings.
-
Pre-screened suppliers: Pre-screening or pre-qualifying the suppliers is another component of procurement administration typically conducted after establishing the control for suppliers. Pre-qualifying the suppliers a company wishes to collaborate with is quite essential. One is able to decide whether the suppliers meet the requirements based on their previous work, the details of the project team, the work process, and many more by doing so. It is basically the process for choosing contractors in which a list of "trusted contractors" is created based on a RFQ or Request for Qualifications. The RFQ normally excludes questions about costs and instead asks for details on previous projects, the project team, and the project process as primary elements to create a prequalification list. The list of requirements typically involves team Project, which is 35%, project approach for 40%, and 25% of past projects.
-
Estimating: Among the crucial components of procurement management is estimation. Estimation refers to the imprecise assessment of something's worth, number, size, or scope. Estimating the project's funding requirements is essential before submitting a bid through the procurement procedure. It is important to weigh and assess elements such as net present value evaluation, budgeting for capital, and cost-benefit assessment when estimating, especially for future references. An estimate is typically created before the project tendering or bidding, confirming whether the funding is accessible or not. Adjustments to the statement of work or SOW must be estimated and allocated with sufficient funds as needed during the project. The total cost typically has to be collated and examined for future use after the supplier has completed their task.
-
Functions and obligations: The procurement administration process is associated with a mixture of tasks and requires different competencies. Accordingly, there are several functions and responsibilities that need to be fulfilled in the purchasing procedure. The positions of the individuals needed to make the procedure work efficiently are specified in a procurement management plan. It outlines the responsibilities and limitations of project managers, contract managers, operational managers, technical managers, and even lawyers.
-
Payments: One of the most critical components in the procurement method is payment. Payments are the sum paid or payables, which refer simultaneously to the act or procedure of paying or being paid for something or someone. The conditions of payment, modalities, and preferred methods must always be included in a procurement management plan depending on the project at hand. It is crucial to include such elements to prevent future disputes and problems. The purchase management plan needs to include information about payment procedures and currencies. The majority of contracts are compensated on an incremental basis, which involves recurrent payments such as monthly remuneration up to a predetermined point. Contractors who believe they have finished a greater job than what an inspector gives them credit for often give rise to issues, even if everything goes according to plan.
-
Management of risk: Risk control is another crucial component for procurement procedures, especially when working with a number of distinct teams. Each project must have a risk profile in a procurement management plan, which includes the risk tolerance, risk level, types of contracts, amount of details, policies in the contract, and reviews on the requirements. The potentiality of threats and the confirmation of the specifications are additionally needed to be included in the profile. The intersection of project and non-project work is frequently the subject of contract legal disputes. The resources or funds that are not required for internal, non-procure activity are needed to resolve these disputes. Additionally, the judgments are viable to be occasionally high in comparison to the project cost.
-
Legal authority: The procurement administration process is essential to be guided by a legal authority. Legal jurisdictions ought to be constantly dealt with in a procurement management plan. It is because it serves to link the project together and inform partners of their work, allowing them to respond appropriately. Significant legal matters, including acquiring environmental licenses, often involve factors other than just the bare minimum of the law, such as monitoring wells, relationships, and many more. The procurement management strategy must meet the minimal legal requirements to guarantee that all partners are aware of them and are able to act accordingly.
-
Limitations and expectations: Plans are continually created while taking various future restrictions and presumptions into account. It comprises normative requirements, timelines, environments, geographical settings, physical circumstances, levels of quality, or safety. A solid procurement management plan often results in a robust procurement procedure, which eventually lays the groundwork for successful project contracting. Nearly all contracts and procurements take place in a setting with several restrictions and presumptions. These restrictions are viable to occur in areas such as legal, schedule restrictions, standards and requirements, budgetary assumptions, and external parties. Constraints due to data integrity, safety, location, ground circumstances, air quality, physical restrictions such as height, width, size of openings, and the like are additionally affected by these limitations.
What are the Key Factors of a Successful Procurement Management?
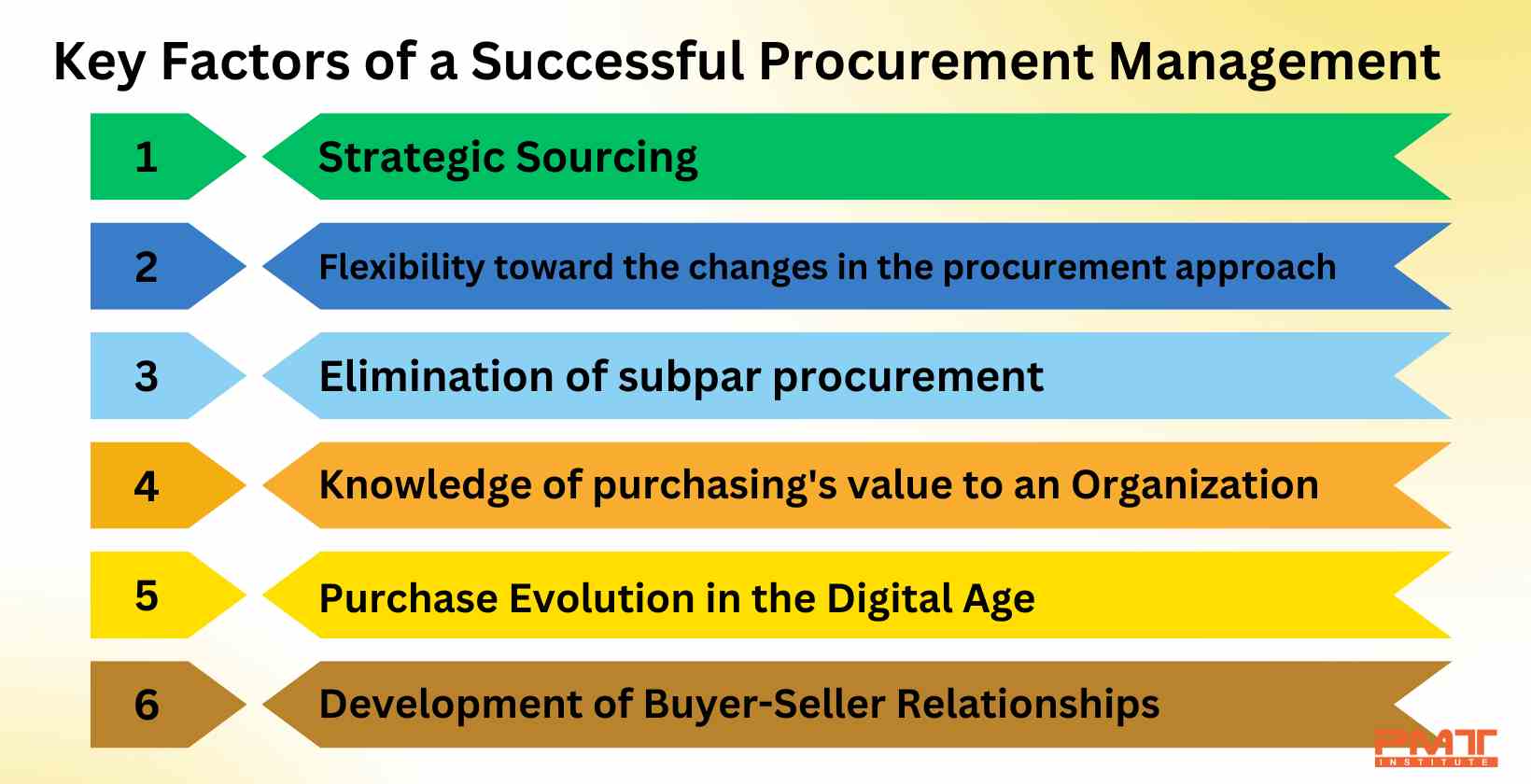
Listed below are some of the key factors of successful procurement management.
-
Flexibility towards changes in the procurement approach: The function of procurement administration has changed significantly over time, and numerous important elements are necessary for its success. Among the crucial elements is the creation of a strategic procurement plan that is in line with the aims and objectives of the company. A thorough evaluation of the company's procurement requirements, the identification of potential suppliers, and the negotiation of advantageous terms and conditions are all included in the plan. The application of technology to procurement administration is another important element in the shifting role of procurement from conventional to modernize. The procurement procedure is greatly streamlined and made easier and more effective through the implementation of e-procurement platforms and other technical tools. Additionally, these solutions give firms improved awareness and authority over the procurement procedure, enabling them to take defensible actions. A shift toward a more cooperative approach with suppliers is also brought about by the shifting role of procurement management. The strategy aims to create lasting, trustworthy connections with providers while acknowledging the crucial function they perform in the organization's success.
-
Strategic Sourcing: The efficacy of procurement management depends on the strategic sourcing applied, which is a key component. It entails finding, choosing, and managing suppliers to ensure the company gets high-quality products and services at reasonable costs. A few of the crucial elements that go into the success of strategic sourcing include supplier preference, negotiating agreements, supplier performance management, partnerships, and cost control. Procurement managers must have a thorough awareness of those goals and objectives in order to properly connect the supplier selection process with the organization's goals. They must be adept at contract negotiations to obtain fair and open agreements that are in the best interest of the company. Making certain that the contracts are enforceable and that suppliers fulfill their obligations. The management of suppliers' performance is regularly assessed by procurement managers, which includes monitoring supplier performance indicators such as delivery schedules and product and service quality. Furthermore, a positive relationship with suppliers must be maintained to ensure that providers are driven to provide high-quality products and services at reasonable prices. The same goes for cost control where procurement managers need to be adept at controlling expenses, which involves negotiating rates with suppliers, overseeing contracts, and keeping tabs on outlays.
-
Elimination of subpar procurement: Inadequate or subpar procurement management usually results in cost overruns, delays, and decreased quality. There are various viable ways to prevent poor procurement from occurring. Some of these methods include strategizing a plan, creating an efficient purchasing approach, and managing contracts, suppliers, and threats in a systematic way. A planned strategy, excellent communication, and solid collaboration between the company and its suppliers are necessary for successful procurement management. Businesses are able to avoid the issues caused by ineffective procurement management and more successfully accomplish their goals by taking into account these crucial considerations.
-
Knowledge of Subpar Procurement's consequences: Unsuccessful procurement management has detrimental effects on a company's finances, the timing of project fulfillment, the quality of its products, its ability to take advantage of opportunities, and many other factors. Negligent procurement management causes the organization to overpay for goods, services, and work, resulting in large financial losses. It leads to diminished market competitiveness and profitability. The organization's capacity to meet deadlines and goals is sometimes impacted by delays in the supply of goods, services, and works, which leads to lesser quality products, increased expenses, and a loss of confidence with clients and stakeholders. It brings an adverse effect on the company's standing and its capacity to provide high-quality goods and services. Legal and contractual problems are potential to arise as well due to poor procurement management. It often leads to situations where contracts may not be clearly established or handled, putting the business at risk of lawsuits and other legal repercussions. Missed opportunities are potential to occur because of poor procurement management since the company is unable to take advantage of the finest suppliers of goods, services, and labor. There is an anticipated decline in competition and a loss of market share if not addressed properly.
-
Knowledge of purchasing's value to an Organization: An organization's purchase and procurement processes are crucial because they lead to cost savings, higher quality, more efficiency, better supplier relationships, and better risk management. It is important for organizations to give procurement management top priority and make sure they have efficient procedures in place. Effective purchase and procurement processes help the organization in terms of saving money by negotiating better pricing for goods, services, and works and avoiding overpayment. It enhances an organization's reputation and its capacity to provide top-notch goods and services. Increased efficiency is attained through efficient purchases and procurement procedures, which enable the company to obtain goods, services, and labor more swiftly and painlessly, freeing up time and resources for other tasks. Businesses are able to set clear expectations and commitments and collaborate with suppliers to accomplish shared goals through effective purchasing and procurement processes, which lead to stronger relationships with suppliers. Furthermore, firms are able to detect and manage risks, such as those related to the quality of the products, services, and activities, delivery schedules, and pricing, because of efficient purchase and procurement procedures.
-
Purchase Evolution in the Digital Age: The latest improvements in technology and the digital transformation have a tremendous impact on procurement management. The procurement process grew in complexity and difficulty while becoming more strategic and important to enterprises. Collaboration and cross-functional teamwork are essential for a procurement management strategy to be successful. To ensure that procurement activities are in line with the company's overall goals and missions, procurement teams must work in conjunction with other departments, including finance, legal, and engineering. Proactive sourcing is a crucial part of procurement management that makes use of suppliers' best prices, qualities, and delivery conditions in the digital age. Relationship management with suppliers is essential to forge solid relationships with suppliers and to regularly assess and improve their performance.
Data analytics and cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming more and more crucial, simplifying procedures, lowering manual labor, and enhancing supply chain transparency.
-
Development of Buyer-Seller Relationships: The process of building relationships between buyers and sellers is essential to effective procurement management. The management of suppliers is a crucial part of procurement management since connection is a fundamental part of supplier relationship management. Both parties can gain a lot from having a good and positive buyer-seller connection, including greater communication, a better understanding of one another's wants and expectations, and an increase in trust and cooperation. Procurement teams need to prioritize open and transparent communication, regular performance assessments, and continual development to build strong buyer-seller relationships. Additionally, they must make an effort to understand the skills, difficulties, and objectives of their suppliers to collaborate with them and develop win-win solutions. Furthermore, procurement teams must take the initiative to tackle any difficulties or concerns that are potential to develop and collaborate with their suppliers to find quick and efficient solutions.
What are the Key Personnel Working with Procurement Management?
There are a number of key personnel working with procurement management. These professionals are normally equipped with the right amount of knowledge, background, and training to be able to employ procurement administration effectively. Some of the common functions involved in procurement management are as follows: procurement manager, procurement specialist, purchasing manager, sourcing managers, purchasing agent, procurement analyst, and procurement buyer.
These job roles are undeniably essential to the successful implementation of the procurement procedure. Each of these roles is associated with responsibilities and tasks that contribute to the fulfillment of the procurement method. Good collaboration and coordination between these job responsibilities are crucial to ensure that procurement activities are efficient, economical, and in line with the organization's goals and objectives.
1. Procurement Manager
A procurement manager is someone who develops and implements procurement strategies, negotiates contracts with suppliers, and oversees the procurement process to ensure that it is in line with the organization's goals and objectives. Their role is to keep an eye on the entire procurement process and ensure it functions well. Additionally, they are in charge of managing the budget for procurement, creating and implementing procurement policies and processes, and ensuring that procurement activities adhere to all applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
The procurement manager is essential to ensuring the success of the procurement process. They are in charge of ensuring that procurement activities align with the company's goals and targets and that it receives high-quality products and services at reasonable costs. A procurement manager must have expertise in business administration, supply chain management, or a comparable discipline. Additionally, they must have knowledge of creating and executing procurement plans, managing supplier relationships, and negotiating contracts.
The duties of the procurement manager include creating and executing procurement strategies, negotiating contracts with suppliers, managing the procurement process, monitoring supplier performance, managing procurement budgetary constraints, and ensuring that all applicable rules and regulations are followed. Strong communication, negotiation, and analytical skills are among the qualities that a Procurement Manager needs to have. They also need to have an understanding of current trends and best practices in procurement, as well as expertise with tools and software related to it.
A procurement manager is viable to be promoted to a higher-level position, such as a Director of Procurement or a Chief Supply Chain Officer, if they have shown great leadership abilities and made significant contributions to the company.
2. Procurement Specialist
The procurement specialist is someone who locates and procures products and services from vendors, negotiates agreements, and manages connections among providers with the goal of aiding in the acquisition method. They collaborate closely with the procurement manager to ensure that procurement procedures align with the company's aims and objectives.
Supporting the purchase procedure is the primary duty of procurement specialists through overseeing daily procurement operations such as market analysis, issuance of requests for proposals (RFPs), and evaluation of provider proposals. They are also in charge of managing supplier relationships and negotiating contracts with vendors to ensure that the organization receives high-quality products and services at reasonable costs.
The procurement specialist is essential to supporting and successfully completing the procurement process as they are in charge of ensuring that procurement procedures are efficient, economical, and in line with the organization's aims and objectives. They must have an expert background in business administration, supply chain management, or a similar discipline, just like procurement managers. Additionally, they ought to have previous experience in market research, managing supplier relationships, and contract negotiations.
Some of the duties that procurement analysts usually perform include conducting market research, issuing requests for proposals (RFPs), assessing supplier bids, negotiating contracts with suppliers, managing supplier relationships, and assisting the procurement manager with regular procurement tasks. Furthermore, the skills that a Procurement Specialist needs to possess include proficiency in negotiating, communication, and analysis, knowledge of current trends and standards in procurement, as well as expertise with tools and software related to it.
The next positions a procurement analyst is able to land after promotion are as a procurement manager or a strategic sourcing specialist. They are usually promoted to a higher-level job for showing great performance and making major improvements to the procurement procedure.
3. Purchasing Manager
The purchasing manager is a professional who acts as a vital member of the supply chain team. Purchasing managers are the experts in charge of finding the best deals on the highest caliber of services and merchandise or equipment, which significantly improves the cost-effectiveness of the company. A knowledgeable purchasing manager is capable of significantly affecting the profitability of a particular company since more than two-thirds of a company's revenues are normally spent on acquired goods and services.
The duty of the purchasing manager is to create a pivotal connection among traders and other participants in the supply chain to offer a range of options for various services and goods. They are essential in the procurement procedure team to guarantee that the purchase is executed efficiently. They make sure that the company receives high-quality products and services at reasonable costs and that purchasing practices are in line with those aims and objectives.
Purchasing managers are generally experts when it comes to corporate governance, supply chain management, or a comparable discipline. Additionally, they possess adeptness in terms of purchasing strategies, maintaining supplier connections, and contractual negotiations. Finding and assessing potential suppliers is one of the primary duties of a Purchasing Manager. However, the level of responsibility assigned to the purchasing manager as well as the kind, size, and geography of the organization all influence other tasks. Senior-level employees are typically in charge of purchasing strategy, along with predicting customer demand for goods and services and pricing patterns. Additionally, they are tasked to operate as a point of contact for clients, team members, manufacturers, and suppliers.
Moreover, they have cross-functional skills in operations management, logistics, and even information technology. Purchasing managers offer excellent leadership skills to the field of procurement. A Director of Purchasing or a Chief Supply Chain Officer are two of the closest potential higher-level positions of purchasing managers. They are normally promoted to a higher-level position once they have shown great leadership abilities and made significant contributions to the company.
4. Sourcing Manager
Sourcing managers are professionals who are in charge of managing the entire sourcing process for the business. They evaluate and enhance sourcing efforts by looking at business expenses, supplier relationships, and new opportunities.
The procurement process depends heavily on the sourcing manager to be successful, making it an important team member. The sourcing manager aids the company in boosting its competitiveness and generating value by locating and acquiring the best products and services at the most affordable pricing.
Sourcing managers must have expert competence in the administration of businesses, management of supply chains, or a similar profession. They need to have prior experience designing and managing strategic sourcing strategies, negotiating contracts, and conducting market research. The sourcing manager must have a thorough awareness of the market, supplier capabilities, as well as the demands and specifications of the company.
The responsibilities of sourcing managers include handling the business's supply portfolio while maintaining expenditure transparency. They create and put into action effective strategies for managing categories and sourcing. They evaluate and estimate the expenses of procurement and make suggestions for ways to cut expenditures. Sourcing managers additionally create bargaining tactics to close lucrative deals, improve sourcing practices for optimal effectiveness, work together with all parties to ensure that terms and procedures are agreed upon, and many more.
Some of the skills that they need to possess are knowledge of sourcing, vendor management, and pertinent software, as well as a deep understanding of how markets work using good business judgment. They need to have strong leadership and project management skills, the ability to maintain and negotiate networking ties, and be capable of gathering, analyzing, and understanding data while being at ease with numbers.
The next position for sourcing managers after a promotion typically includes a Chief Supply Chain Officer position or a Vice President of Procurement role. A Sourcing Manager is promoted by showing good performance and making substantial contributions to the firm.
5. Purchasing Agent
A purchasing agent is a procurement professional who is tasked with locating items for a business, whether they are intended for internal use or resale. They track down sources, do product and service studies, and handle orders.
The purchasing agent's role is mainly to locate and obtain products and services from suppliers. They negotiate agreements and handle supplier relationships to assist with the purchasing procedure. They collaborate closely with the purchasing manager to ensure that purchasing activities are in line with the aims and objectives of the firm.
Purchasing agents are undeniably important to the administration of the procurement method. They ensure that purchasing operations are efficient, affordable, and reasonable while supporting the success of the company overall. They are typically adept when it comes to supply management, business administration, and market research.
There are a lot of responsibilities piled up for purchasing agents. Some of these responsibilities include creating profitable sourcing techniques, examining offers and supplier profiles, and preparing for or utilizing successful negotiating strategies. Purchasing agents are tasked with maintaining connections with important suppliers to ensure product quality, prompt delivery, and compliance with agreements as well.
Some of the most important skills that every purchasing agent needs to have are the following: a demonstrated competence in a purchasing agent position or equivalent, a track record of successfully negotiating costs and terms and conditions, an understanding of data analysis, market research, and optimum purchasing habits. Being able to understand purchasing applications such as SpendMap and adeptness in Microsoft Office are essential abilities for a Purchasing Agent.
A purchasing agent is viable to be promoted to a higher-level job, such as a Purchasing Manager or a Sourcing Manager, for their reliable performance and significant contributions to the purchasing procedure. Additionally, they have the potential to advance to a senior management role, such as a Director of Purchasing or Chief Supply Chain Officer, provided that they have good leadership and strategic thinking abilities.
6. Procurement Analyst
The procurement analyst is someone who finds trustworthy vendors and suppliers for a business by using thorough analysis. They usually coordinate with suppliers as they compare and analyze product samples. Establishing acquisition agreements on the company's behalf is one of the procurement analysts' typical activities.
The function of the procurement analyst is to assess the offerings from providers. Interacting with vendors, assessing goods, negotiating supply agreements, and creating cost reports are just a few examples of their specific duties.
The procurement analyst plays a crucial part in guaranteeing the success of the procurement process by offering insightful analysis and suggestions based on data they have gathered. They assist in making wise judgments, reducing costs, and improving competitiveness for the procurement department.
A specialist in procurement is necessary to possess expertise in data analysis, supply chain management, or a related field. They must possess knowledge of current trends in procurement as well as exposure to data analytics platforms and technologies. The procurement analyst additionally ought to have great presentation skills and the ability to communicate efficiently and offer relevant suggestions to the procurement division along with other partners.
Procurement analysts have a lot of tasks to execute. They are responsible for identifying supply requirements and investigating promising suppliers. They serve as points of contact for suppliers and vendors when conveying pricing details and performance reports. Procurement analysts are obliged to locate vendors, evaluate their product samples, and keep track of the attributes and advantages of services and goods.
Cost-benefit analysis is typically crafted by a Procurement Analyst for managers to study.
Some of the pertinent skills that procurement analysts need to embody are the following: competence with analytical software and computerized procurement, comprehensive understanding of supply chains, corporate leadership, and strategic purchasing, and superior abilities in analysis and negotiation. A procurement analyst must be skillful in terms of interpersonal connections and corporate communications.
The higher-level job titles that procurement analysts are able to land after a promotion include Procurement Specialist or Procurement Manager. They are viable to take senior managerial positions as well, once they showcase exceptional performance. These positions include Director of Procurement or Chief Supply Chain Officer.
7. Procurement Buyer.
A procurement buyer is responsible for managing a company's purchases of services and goods. Procurement buyers investigate the providers of the items acquired and establish contracts to get the best price for the business. They sometimes monitor orders to make sure they are delivered as intended.
The role of procurement buyers is generally to supervise the ordering of products and services for the business. They are the ones who get in touch with potential suppliers when purchase requests from staff members or departments are released. They evaluate the price quotes provided by these vendors and select the most economical choice.
Procurement buyers are vital members of the procurement team. They ensure that the company receives high-quality products and services at affordable prices. The procurement buyer helps guarantee that procurement activities are efficient, economical, and in line with the business's goals and objectives by negotiating agreements and handling supplier connections.
The procurement buyer is responsible for a number of tasks. One of which is to establish indirect expenditure category management while taking the lead in RFP management and execution. Procurement buyers, additionally, handle logistics, inventory control, storage, manufacturing planning, and scheduling tasks. They establish working relationships with many suppliers while providing top-notch customer service during the RFI, RFP, and RFQ processes. Regular checking and modification of the MRP components' policy report is assigned to a Procurement Buyer at the same time.
Procurement buyers must be skillful in using procurement software and tools, as well as in communication and negotiation. They need to display adeptness in assessing data and making defensible conclusions. They must be well-versed in trends and efficient methods in procurement as well. Additionally, the procurement buyer must be a strong communicator as they are in the business of interacting with suppliers and other stakeholders frequently.
A procurement buyer is promoted to a higher-level job, such as a Procurement Specialist or a Procurement Manager, once they show reliable outputs and significant impact on a company. They are viable to move to even higher positions such as Director of Procurement or Chief Supply Chain Officer with great performance and influence.
How to Build a Procurement Management Plan?
A procurement management plan is a type of tool that controls the procedure for locating and choosing a supplier. A procurement management plan provides the project's purchasing foundation. It is updated as procurement requirements change and acts as a manual for handling purchases of products, materials, and/or services over the course of a project. A procurement management plan is what is used when the procurement management procedure is set out on paper or a document for teams to follow.
Listed below are some of the steps on how to build a procurement management plan:
-
Create templates for terms. The procurement management plan is normally started by outlining the parameters of the procurement. It is when the specific procurement details are listed, as well as the name of the procurement personnel, the importance of the procurement, and the schedule set for its fulfillment. This information is utilized when a purchase order is at hand.
-
Create dynamic agreements. It is necessary to choose the type of agreement and the administration method. Everyone agrees to the terms of service through the contract. Some of the various contract types include fixed price and cost reimbursement agreements.
-
Distinguish and reduce risks. It is crucial to identify and document any potential risks during the procurement. Each issue must have a solution once a complete list has been compiled. It is beneficial to delegate a team member with risk mitigation, so they take responsibility for completing the assignment.
-
Resolve cost. It is wise to be aware of the project procurement expenses. It must be detailed and comprehensive. It is probable that a request for proposal or RFP is going to be issued once the costs have been determined. The vendors then return with their prices for the goods or services.
-
Determine restraints. Any constraints must be identified prior to project commencement to prevent being caught off guard by unanticipated restrictions later on. The prices, scope, resource limitations, and technical requirements are a few of the procurement-related restrictions that need to be considered. The list is viable to be consulted at any time during the various project phases once completed.
-
Get contract approval. It is crucial to ensure that all parties who must monitor the agreement's approval are informed and able to participate. Procurement professionals must analyze the services and costs after reviewing the bids. The bids must then be submitted to the decision-makers in the project team for consideration.
-
Establish choice standards. Procurement professionals need to establish standards that allow them to choose which bid to accept. These standards ought to be available to everyone reviewing the bid so they are able to gauge their performance.
-
Establish a vendor management plan. The procurement management strategy transitions into a vendor management plan after the signing of contracts. A management strategy for the suppliers aids in ensuring that products and services are supplied on schedule and in accordance with specifications.
1. Create Templates for Terms.
The initial stage of creating a procurement management strategy is to create templates for terms used. It entails creating standard terminology and vocabularies that are going to be used in purchase orders, agreements, and request for proposals (RFPs). These templates shorten the time and effort needed to create procurement records, ensuring that all of them utilize the same language and simplify the procurement procedure.
The creation of templates for terms is crucial for the formulation of the procurement plan. It is one way to standardize the procurement procedure and guarantee that all parties participating have a clear grasp of the terms and conditions. By employing a consistent language in all procurement documents, term templates serve to lessen the likelihood of misunderstandings and disagreements between the customer and the vendor.
It is essential to create templates for terms since doing so guarantees uniformity throughout all procurement records, clarifies the conditions for all parties concerned, and lessens the likelihood of misunderstandings and disagreements. Standardizing language in the procurement process contributes to a reduction in the time and effort needed to create the paperwork.
Procurement teams expect to have a streamlined and effective procurement process that leads to more successful contracts and fewer misunderstandings between partners. The adoption of templates for terms leads to cost savings and ensures that everyone involved in the procurement process is aware of the terms and conditions. It fosters goodwill and successful collaboration between the purchaser and provider.
2. Create Dynamic Agreements.
The subsequent step in crafting a procurement plan is to create dynamic agreements. Such a step involves choosing the form of contract or agreement to be employed in the procurement to obtain the necessary products or services. Choosing the type of contract, such as standardized price, cost reimbursement, time and materials, or incentive-based contract, is part of the process.
The procurement process, in its entirety, benefits from describing the type of agreement since it helps to determine the conditions and limitations of the agreement that exists between the purchaser and provider. Outlining or creating agreements ensures that each party is aware of their obligations and expectations as stated in the contract. Additionally, it helps reduce the likelihood of misconceptions or conflicts, which often cause delays or failure in projects.
There are several necessities associated with the creation of dynamic contracts. Some of these necessities include understanding the project's scope to choose the sort of agreement that best suits the demands of the project. The degree of risk involved must be taken into account as well when choosing the form of agreement. For instance, a fixed-price contract is preferable for low-risk projects, while cost-reimbursement contracts are better suited for high-risk projects.
Defining the deliverables is necessary to choose a contract that matches each party's expectations and obligations. The same goes for assessing the budget to choose a contract that is economical and adheres to the set budget. Furthermore, verifying that the agreement conforms to all applicable laws and regulations by reviewing is additionally necessary. Procurement teams can choose the type of agreement that best suits the demands of the project and guarantee a smooth procurement process by taking these considerations into account.
Procurement teams anticipate having a thorough and transparent procurement process that satisfies all the goals of the project by defining the type of agreement. Selecting the right kind of agreement helps lower risk and ensure that needs are met promptly and affordably.
3. Distinguish and Reduce Risks
A procurement management plan is subsequently built by distinguishing and reducing risks. It is an essential component of the procurement management plan that enables enterprises to obtain the goods and services required for their operations with the least amount of issues.
The act of determining procurement threats and employing ways to reduce them brings a number of benefits to the entire procurement management planning process. One of which is that it lessens the likelihood of monetary losses due to procurement failures, such as subpar items, delayed deliveries, or contract disputes, by identifying and eliminating risks.
Organizations are able to lessen the likelihood of monetary losses due to procurement failures, such as subpar items, delayed deliveries, or contract disputes, by identifying and eliminating risks. Companies can increase the effectiveness of their procurement process and ensure it complies with legal, regulatory, and ethical standards by recognizing and eliminating any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and delays. Additionally, reducing procurement-related risks helps preserve their reputation and the trust of their stakeholders.
The necessities required to effectively determine and reduce threats include knowing the procurement procedure in a deeper way. The potential risks must be identified first before they are analyzed. Procurement professionals must then craft ways on how to mitigate the threats based on the analysis conducted.
An efficient risk-reduction and risk-diminishing procurement management strategy often lead to the following: increased supplier performance, savings from expenses, compliance with laws and standards, and a better reputation.
4. Resolution of Cost
The next step for creating a procurement plan is to make a resolution of cost. Establishing costs is essential when creating a procurement management plan. The procurement process must stay within budget and give the business the greatest potential return on their money.
The preparation of a resolution of cost when building a procurement management plan holds a lot of importance for the whole procurement procedure. These things include being able to clearly define and formulate the purchasing budget, guaranteeing the right value for their money, preventing unnecessary expenditures, and facilitating reasonable financial decisions.
It is necessary for every procurement professional to understand the procurement method itself in order to resolve costs. The costs involved in every stage of the procedure must be identified and analyzed accordingly. Companies must then develop a budget that covers the costs that have been identified.
The potential outcomes of defining the costs involved in the procurement plan include budget control, cost savings, and enhanced efficiency. Companies control the procurement process's budget and avoid going overboard by establishing costs. They are able to locate areas where they need to save money and create plans to lower the price of their purchases. Additionally, businesses are able to streamline their procurement procedure and ensure it is as effective and economical as possible by doing so.
5. Determine Restraints
Procurement experts must identify restraints to create a purchase management strategy. Identifying the project restraints means recognizing and acting on any restrictions or limitations that have an unfavorable impact on the acquisition procedure. Budgetary constraints, legal controls, technological limits, and the availability of resources are just a few of the different types of restrictions that are present.
The act of understanding limitations is crucial as they significantly affect the acquisition procedure and the project's overall performance. Budgetary restrictions, for instance, restrict the available possibilities for procurement, while legal limitations set limits on the techniques that are applied. Technical limitations affect the timetable for procurement activities, while resource availability influences the purchase of specialist goods or services.
A full comprehension of the project needs, an in-depth understanding of the constraints and boundaries, and a strategy for dealing with these constraints are necessary for identifying restraints in the procurement management plan. It is additionally crucial to incorporate a risk management plan to address any potential hazards connected with the restrictions and limitations.
An improved procurement procedure, reduced risk, and a higher chance of success are potential results of successfully identifying and managing the limitations in the procurement management strategy. Early recognition of these limitations enables the procurement management plan to be modified at the earliest time, which lessens the effects of potential project constraints and guarantees the success of the procurement procedure.
6. Get Contract Approval
Another important step in the creation of a procurement management plan is to get the contract approved. It is necessary to ensure that the procurement management strategy is well-structured, supported, and resourced.
The approval of contracts is quite important for building a procurement management plan. It aids in ensuring that the procurement procedure is open, competitive, and just. It helps chosen suppliers provide the necessary products and services with the needed quality and within the required timeframe.
A thorough and organized procurement management plan that satisfies the requirements and demands of the company is the main condition for getting the contract approved. Details about the procurement timeline, technique, evaluation standards, and the functions and duties of the procurement team and stakeholders must all be included in the strategy. Senior management, the procurement department, the legal department, and the finance department must all evaluate and approve the procurement management strategy. Such a stage is essential to ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding the procurement strategy and that the plan has the backing and resources it needs to be successful.
The potential results of getting the contracts approved include enhanced purchasing accuracy and efficacy, reduced purchasing expenses, and better value for money. A well-organized procurement management strategy aids in ensuring that the selection of suppliers is fair, productive, and transparent, and that they are able to provide the requested products and services on time and to the required standard.
7. Making Choice Standards
Procurement professionals can create effective procurement management plans by establishing choice standards or decision criteria. Decision standards are usually used to select the best bids or proposals received from potential suppliers. These proposals are evaluated and weighed using the decision standards.
It is important to establish choice standards while building the procurement plan to guarantee that the procurement process itself is fair, open, and productive. The decision-making criteria are crucial because they offer a framework for assessing and comparing the bids or proposals obtained from potential vendors. The choice standards must be clearly specified, objective, and explicit.
The main prerequisite for formulating decision criteria is a clear understanding of the organization's demands and specifications. The choice standards that assess the bids or proposals received from potential vendors must be created using this information. The criteria should be relevant, measurable, and aligned with the aims and objectives of the business.
Some potential results of establishing choice standards for a procurement management plan are improved procurement quality and efficacy, decreased procurement expenses, and reasonable financial returns. A clearly defined set of choice criteria makes it attainable to ensure that the procurement process is transparent, productive, and equitable.
8. Establish a Vendor Management Plan
The final phase in the creation of the procurement management plan is to establish a vendor management plan. The vendor management strategy describes the methods and tactics a company employs to manage its relationships with suppliers and ensure they provide the essential products and services promptly and according to the specified standards.
The creation of a vendor management plan is crucial because it offers a structure for managing the connection between the business and its trading partners. The company's strategy and tactics for ensuring that its suppliers provide the needed products and services, which correspond to the quality and schedule being specified, are described in the vendor management plan.
The primary requirement for creating a vendor management plan is to have a clear understanding of the organization's demands and specifications, as well as the requirements of the suppliers. A plan that specifies the obligations of the company and its vendors and ensures that the relationship between them is in line with those aims and objectives must be created.
Implementing a vendor management plan allows businesses to experience improved purchasing productivity. An organized vendor management strategy makes it easier to ensure that the company's connection with its suppliers is effectively managed, relatable, and compliant. These factors result in better supplier performance, lower risks, and better financial value.
How Can Procurement Management Improve?
Procurement management improves the procurement process in several aspects. There are eight viable ways in which procurement management can enhance the procurement process itself. These steps involve investing in a platform for online adoption, establishing strategic sourcing guidelines, maintaining communication with teammates, and controlling inventory. Choosing the appropriate digital instrument for procurement, streamlining procedures, automating laborious processes, and enhancing worker training are also included in these steps.
Investing in a digital adoption platform (DAP) that is packed with interactive walkthroughs created with users and tools in mind allows procurement teams to onboard, train, and operate simultaneously. Procurement professionals can establish sourcing guidelines through the use of a SWOT analysis. One can make changes to any existing procurement rules based on the identified threats. New policies will be more in line with business requirements when working on the existing ones.
Furthermore, maintaining open lines of communication with the staff helps procurement professionals achieve long-term success by ensuring that all parties are on the same page. The most accurate way to manage inventories is by using inventory management tools. Using tools that are best suited for the company reduces human errors that are often evident in orders, stocks, raw materials, etc. Choosing a centralized purchasing solution increases the team's overall productivity and focus as they won't have to manage multiple tools at once.
Moreover, optimization is a technique that most business units can utilize. Standardized procedures make it simpler to monitor results by establishing norms and benchmark criteria. Using automated assistance for difficult tasks helps professionals in the procurement field save time throughout the year. The use of interactive tutorials and round-the-clock support in a digital adoption platform can autonomously and instantly train and onboard users from any location.
One of the most recent innovations to aid in the procurement procedure is through the use of procurement software. Procurement management software is an electronic solution that dramatically enhances and shortens the processing time for procurement. It typically works by automating many of the manual and labor-intensive procedures involved in the procurement process, from sourcing to contract administration. Such software makes the entire procurement process more efficient, and additionally assists businesses in selecting suppliers, negotiating agreements, and developing procurement strategy.
What Training and Certifications are Required for Procurement Management?
Here are some of the training and certifications required for procurement management:
-
Certified International Procurement Professional or CIPP: The CIPP is an online procurement certification program for those who are completely new to procurement or have fewer than five years of experience. It covers purchasing strategies, negotiation tactics, legal considerations, contract management foundations, contract term strategy, cost concepts, operational procurement, and finance. The course is suitable for those with some prior experience in the field of procurement who simply wish to develop their abilities holistically and earn international certification. There are institutions that facilitate the provision of such certificates for $2,195, which includes 12 months of unrestricted online access.
-
Certified International Advanced Procurement Professional or CIAPP: The advanced learning session for CIPS is called Certified International Advanced Procurement Professional Training or CIAPP. Professionals who successfully complete the course are awarded an Accredited International Procurement Certification. Among the procurement skills taught in such a curriculum are advanced Procurement, Negotiation techniques, Basics of Contract Management, Legal Aspects of Procurement, Operational Procurement, Strategy for Contract Terms, Cost Concepts for Procurement, and Finance. The certification itself is extremely challenging to obtain without the aid of literature or extensive experience gained through international travel. However, anyone who completes it is expected to either be promoted to desirable positions or be able to secure well-paying procurement jobs. The usual fee for the CIAPP certificate amounts to $2,195 with unrestricted online access for 12 months.
-
Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply or CIPS: The nonprofit organization known as CIPS or Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply provides relevant procurement and supply management certifications, education, and training services. Employers consider CIPS a premier source of information on supply and procurement. There are six highly regarded and sought-after CIPS credentials, including levels 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. The procurement skills taught depend on the level of training a person has. Level 2 is suitable for people who are new to the procurement sector. The advanced levels, such as the level 6 and 7 certificates, which are the most comprehensive CIPS qualifications a person can pursue, cover everything one needs to know about procurement. The fees start at $1,100 and go up to $2,700 depending on the desired level.
-
Certified Procurement Operations Specialist or CPPOS: The Next Level Purchasing Association or NLPA offers the Certified Procurement Operations Specialist or CPOS credential. The certification demonstrates one's understanding of negotiating techniques, approaches for enhancing supplier performance, and sourcing and procurement tactics. The NLPA offers several certifications, with CPOS serving as the first level. The CPOS certification requires passing an examination and completing an online course.
-
Certified Procurement Operations Manager or CPOM: The NLPA offers the Certified Procurement Operations Manager or CPOM. The certification, which is the NLPA's third level, builds upon the skills gained through the CPOS and CPOP certifications. The CPOM certification focuses on developing collaborative skills to work well with other departments and achieve the best results and a better bottom line. The credential requires passing an exam as well as completing online coursework.
-
Certified International Procurement Manager or CIPM: The CIPM certification, powered by IPSCMI, is the most potent procurement certification program available. It provides in-depth knowledge of the entire procurement cycle procedure, global sourcing, and the most recent trends and methods for purchasing and supply chain management in a global setting. These topics are covered from the fundamental level to the expert phase. Newcomer supply chain and procurement professionals seeking to expand or enhance their expertise are suitable candidates for the Certified International Procurement Manager (CIPM) certification.
Is Procurement the Same as Purchasing?
No, procurement is not the same as purchasing. Purchasing and procurement are two linked but separate procedures that make up a company's supply chain management.
The act of acquiring products, services, or materials from outside sources is referred to as purchasing. It is a tactical function that concentrates on purchasing the right goods at the right time and price to meet the needs of the firm. Creating purchase orders, assessing suppliers, negotiating prices, and monitoring delivery schedules are all standard aspects of the purchasing process.
On the other hand, the term "procurement" refers to a broader range of operations, such as planning, sourcing, buying, and managing contracts, that are involved in acquiring goods, services, and materials. It is a systematic role that aims to enhance the overall performance of the supply chain, reduce risk, and increase value for the company. Supplier relationship management, contract administration, cost evaluation, and supplier selection are additional procurement operations.
Procurement encompasses all operations related to acquiring products, services, and materials, whereas purchasing focuses on the acquisition of goods. Excellent purchasing capabilities are necessary for effective procurement, but it also requires strategic management of the entire supply chain.
Does Procurement Management Include Inventory Management?
No, procurement management does not inherently include inventory management. Inventory management and procurement management are two distinct but connected tasks within supply chain management.
Inventory management focuses on controlling the flow of items within a company, including storage, movement, and control of inventory levels. Procurement management, on the other hand, concentrates on procuring commodities, services, and materials from outside suppliers.
However, there are aspects of inventory management that ensure inventory levels are sufficient to meet demand and control the flow of products from suppliers to the organization's facilities. In some businesses, these aspects are included in procurement management. However, this depends on the specific procedures and roles within the business.
Inventory management, in general, ensures the right amount of items are available at the right time to satisfy consumer demand, whereas procurement management focuses on ensuring the supply of commodities to the company. Effective inventory management and procurement management together ensure a seamless and successful supply chain, reducing costs and increasing customer satisfaction.
The two roles are distinct and require different procedures, competencies, and roles, despite some overlap with procurement management. Both inventory management and purchasing management are critical for the organization to succeed overall and effectively manage the supply chain.
Does Procurement Management Include Purchasing Management?
Yes, purchasing management is part of procurement management. The term "procurement management" is more general and refers to all operations involved in obtaining products, services, and works from outside vendors. It encompasses every step of the process, from determining the demand for an item or service to evaluating and selecting suppliers, negotiating a deal, and ensuring the delivery of goods or services meet the necessary quality standards.
On the other hand, purchasing management is a specific facet of procurement management that deals with the actual process of purchasing goods and services. It involves tasks such as creating purchase orders, generating buy requisitions, receiving and inspecting items, and compensating vendors.
Every company requires procurement management to ensure the correct products and services are purchased at the right time, price, and quality. Efficient procurement management helps businesses reduce costs, improve supplier relationships, and ensure compliance with procurement rules and regulations.
Purchasing management, as a component of procurement management, is essential to ensure the efficient and effective acquisition of products and services. Companies that implement optimal procedures in procurement management are better equipped to achieve their goals and thrive in today's competitive economic climate.
Do Procurement Management Courses Exist?
Yes, there are courses on procurement management, which is a well-established field of study. The purpose of procurement management courses is to equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary for efficiently managing procurement activities.
Some of the typical topics covered in procurement management courses include understanding the relationships between businesses and their suppliers, the definition of supply chain management, and how to control the flow of products and services from suppliers to consumers. Strategic sourcing, which involves creating strategies for purchasing products and services in line with a business's objectives, is also included in the course.
The courses also cover contract management, which includes negotiating and overseeing agreements with suppliers, as well as tracking performance and resolving disputes. Building and maintaining productive relationships with suppliers, analyzing and selecting suppliers, and managing supplier risk are also addressed.
The courses explain the methods and steps involved in procuring products and services, such as creating purchase orders and managing invoices. Compliance with procurement policies, laws, and other legal and ethical issues are also part of understanding procurement regulations and ethics covered in the program.
There are various levels of procurement management education available, ranging from undergraduate to postgraduate degrees and professional certifications. These courses are suitable for those looking to pursue careers in procurement, as well as professionals already working in the field who want to enhance their education and professional growth.
A comprehensive understanding of the procurement process, supplier relationships, and the legal and ethical aspects of procurement is essential for success in the complex and critical field of procurement management. By taking procurement management courses, students can acquire the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the industry and make a positive impact on their organizations. Procurement management courses are a valuable investment in your future, whether you are starting your career or seeking to upgrade your current skills.
Final Thoughts
Effective procurement management is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation and success of any project. By understanding its processes and benefits, project managers can streamline operations, reduce costs, and build stronger supplier relationships.
With the right training and certifications, procurement professionals can enhance their skills and contribute significantly to their organization's success. Embrace procurement management as a strategic asset and leverage its power to drive your projects to successful completion.






