What is Inventory Management? Definition, Types, Key Elements & Components
Published:
Updated:
Inventory management involves tracking and managing a company's raw materials, WIP, and finished goods. It means making sure that the right products are offered in the right amounts, at the right time and place, and at the right price. The goal of inventory management is to keep the right amount of stock on hand to meet customer needs, keep prices low, and make as much money as possible.
There are a few key parts of managing goods that are important to its success. Some of these factors are predicting demand, planning inventory, tracking and controlling inventory, and optimizing inventory. Demand forecasting is the process of figuring out what customers are going to like to purchase in the future. It helps a company figure out how many goods to keep on hand.
Inventory planning is the process of figuring out how much inventory to order or make based on expected demand and other factors. Inventory tracking and control involve keeping an eye on inventory levels and making sure they are handled well, while inventory optimization involves making sure that inventory management is as efficient and profitable.
A company is able to utilize different types of inventory management methods based on its needs and goals. These include just-in-time (JIT) inventory management, economic order quantity (EOQ) inventory management, and materials requirement planning (MRP) inventory management, among others. Each type of inventory management has its own benefits, such as lowering inventory prices, improving cash flow, and increasing productivity.
Table of Contents
What is Inventory Management?
Inventory management includes managing a company's raw supplies, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Maintaining stock quantity, placement, and timing. It is used to provide clients with the right products at the right timing, quantity, and price. Its key objective is to meet client demand while minimizing costs and saving money.
Inventory management includes forecasting, planning, procurement, tracking, and optimization. Demand forecasting predicts customer purchases. It helps businesses determine inventory. Inventory planning determines how much to buy or manufacture based on demand, lead time, safety stock, and order cycle. Procurement supplies inventories to fulfill demand. It involves picking a seller, ordering, and receiving. Inventory tracking involves managing inventory levels. Inventory optimization maximizes efficiency and profit.
Selling physical goods requires good stock management. It helps organizations match inventory prices to consumer demand, avoid stock-outs, and maximize inventory utilization. Inventory management improves cash flow, working capital, and productivity. Poor inventory management causes stock-outs, overstocking, higher keeping expenses, and lost sales, which affect a company's profits.
How does Inventory Management work?
Inventory management is a complicated process with many steps and functions. Demand forecasting is the first step. It is figuring out how many goods customers want in the future. The data is then used to create an inventory plan that sets goal inventory levels, safety stock levels, and reorder points.
Businesses begin the buying process once it has an inventory plan in place. It entails getting the inventory things needed to meet customer demand. Procurement Management involves buying items from suppliers, making things in-house, or mixing both. Businesses must build strong ties with their suppliers, monitor lead times, and track inventory levels to ensure that procurement goes smoothly.
Tracking goods is an essential part of managing them. It means keeping an eye on inventory levels to make sure it stays at the right amounts. Businesses use various tools like inventory management software, barcoding systems, and radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology. These tools let companies track inventory levels in real-time, find discrepancies in inventory, and change inventory levels accordingly.
Lastly, inventory optimization makes inventory management efficient and profitable. It involves looking for ways to lower inventory costs, such as using just-in-time (JIT) inventory management or shortening lead times. It consists of finding ways to move more goods, such as by running sales or improving the production process.
Overall, effective inventory management gives numerous benefits to businesses. Businesses reduce costs, minimize stock-outs, and improve customer satisfaction by maintaining optimal inventory levels. Furthermore, companies gain valuable insights into their inventory processes, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that lead to improved profitability and growth by using inventory management tools.
What is the importance of Inventory Management in Project Management?
Managing inventories is an essential component of project management because it secures the availability of all components, including the human resources and physical materials, required to finish a project on time and within budget. Effective inventory management enables project managers to strike a balance between the need for acceptable inventory levels and the requirements for cost control and the avoidance of stockouts, delays, and other difficulties that influence the completion of the project.
The management of inventories is an important aspect of project management since it helps to guarantee that all the necessary features and resources are accessible at any given time. It encompasses everything, from unprocessed materials and tools to completed goods and replacement components. Project managers are able to avoid delays and reduce the danger of stockouts or shortages, both of which have the use to influence the project's timeline and budget if it maintains ideal inventory levels.
A lack of effective inventory management results in overstocking or stockouts, either of which results in unneeded holding expenses or missed revenues. Efficient management of inventory assists firms in lowering operating expenses, maximizing productivity, and enhancing their level of service to customers.
What is the purpose of Inventory Management?
Inventory Management aims to guarantee that a business has the appropriate amount of inventory, at the appropriate location, at the appropriate time, and for the appropriate price. The fundamental objective is to keep the right amount of inventory on hand to satisfy customer demand while minimizing inventory holding costs and optimizing profitability.
Businesses that sell tangible things need to manage their inventories well since it has a direct impact on customer happiness, revenue, and overall effectiveness. Businesses meet client requests while limiting the expenses of retaining inventory by maintaining optimal inventory levels, along with ensuring that it has the supplies and resources needed to do so.
Additionally, inventory control is vital to the efficient operation of the production process. Businesses avoid stock-outs, decrease waste, and shorten lead times by controlling inventory levels correctly. Inventory management helps companies streamline their production procedures, enhancing customer satisfaction, and boosting revenue.
A business's supply chain is better understood through inventory management, which enables it to pinpoint problem areas and streamline its processes. Businesses track inventory levels in real-time, spot inventory inconsistencies, and modify inventory levels as necessary by employing inventory management software and other tools. Making data-driven decisions with the use of it increases profitability and growth.
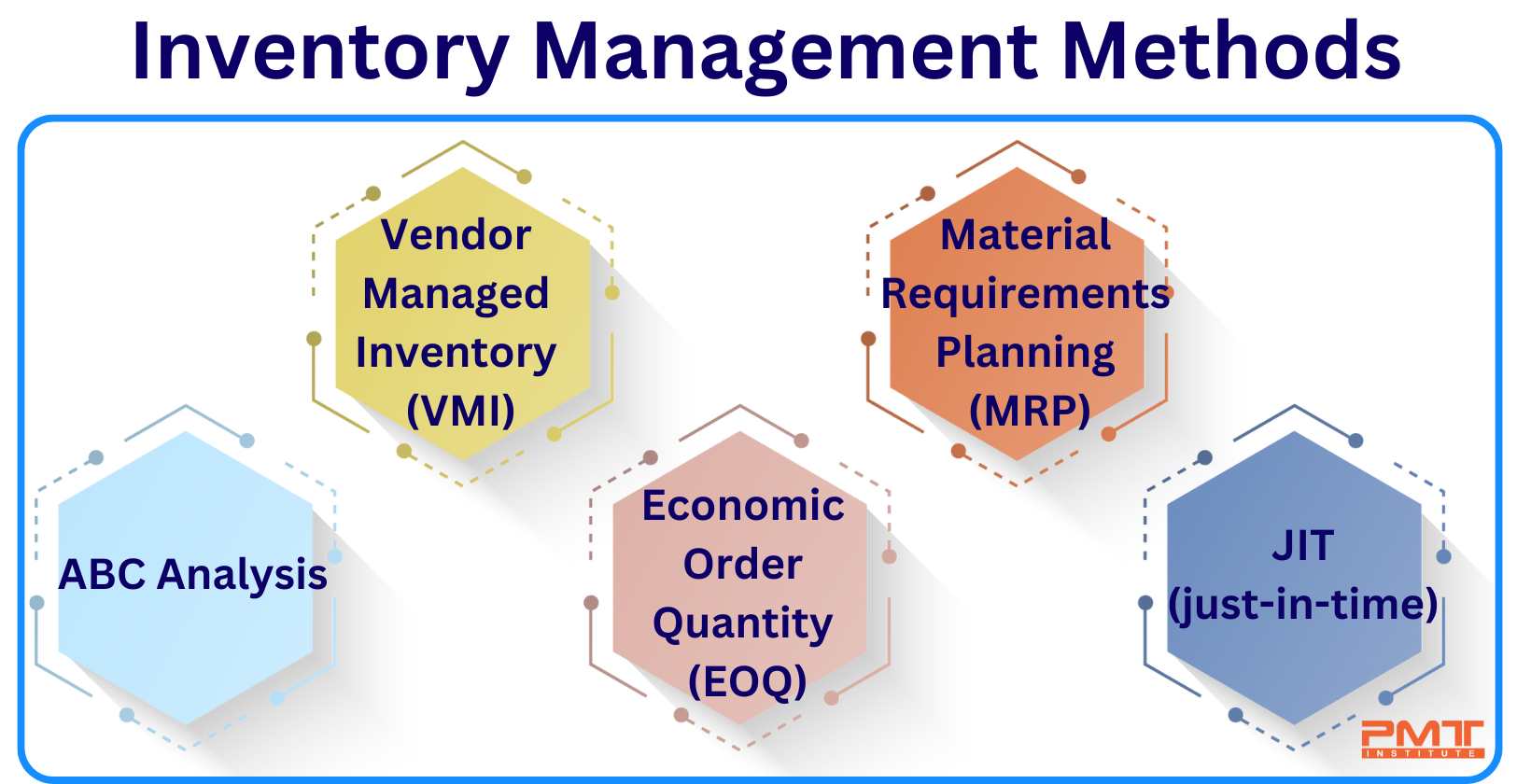
What are the different Types of Inventory Management Methods?
Listed below are the different types of inventory management methods.
-
ABC Analysis: It classifies inventory items according to their worth and degree of significance to the company. A, B, and C are the three groups into which the objects are split, with A items being the most valuable and C items being the least. It allows companies to focus on the most critical inventory products and prioritize their inventory management activities.
-
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): The supplier takes control of the customer's inventory levels. The supplier keeps an eye on inventory levels and tops them off as necessary, which helps firms cut expenses associated with maintaining goods on hand and boost supply chain effectiveness.
-
Material Requirements Planning (MRP): The technique uses a computerized system to plan and manage the inventory needed for production. The ideal inventory levels required to satisfy consumer demand are determined by considering variables, including production schedules, lead times, and inventory levels.
-
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): The technique determines the ideal order quantity required to reduce inventory holding costs while ensuring adequate stock is on hand to meet customer demand. The perfect order quantity is chosen to consider carrying fees, demand rates, and order costs.
-
JIT (just-in-time) inventory management: The strategy forgoes stockpiling extra inventory instead of ordering what is required. Suppliers and businesses must work together carefully to ensure that stock is supplied on time and in the right amount. JIT helps companies in cutting inventory holding expenses and enhance supply chain effectiveness.
1. ABC Analysis
An inventory management technique known as ABC Analysis includes classifying inventory items according to their worth and level of significance to the company. The Pareto principle, which claims that roughly 80% of outcomes result from 20% of causes, is the foundation for that approach. It implies that a small fraction of inventory products account for a significant portion of the expenditures associated with managing inventory.
The ABC Analysis classifies inventory goods into three categories, A, B, and C, according to their worth and degree of significance to the company. The most valuable and significant things, or A items, often make up a tiny portion of the inventory items but are responsible for a significant portion of the inventory expenditures. B items make up a higher portion of the inventory items and expenditures and are of medium value and importance. C items aren't very valuable or important, and there are a lot of them, but it only cost a small portion of the inventory prices.
The ability to concentrate inventory management efforts on the most essential inventory items makes ABC Analysis an efficient inventory management technique. Businesses make sure that they are maintaining optimal inventory levels for the products that are most crucial to their operations by focusing their inventory management efforts on A item. It helps organizations lower the expenses of maintaining inventory, reducing stock-outs, and raising customer satisfaction.
Walmart is one company that makes use of ABC Analysis. Walmart employs that method to control inventory levels and guarantees that the most crucial goods are constantly in stock. Walmart decreases the stock-outs, raises customer happiness, and cuts expenses associated with maintaining inventory by concentrating on A goods. It aids Walmart in improving profitability and gaining a market advantage.
The ABC Analysis is a useful inventory management technique that enables companies to classify inventory items according to their worth and level of relevance. Businesses optimize inventory levels, cut expenses, and boost customer satisfaction by concentrating on the most important inventory products. Walmart is one of the companies that use ABC Analysis. It has successfully used that technique to enhance its inventory management procedures and obtain a competitive edge in the market.
2. Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) refers to a method of inventory control in which the supplier manages the consumer's inventory levels. It is a system that allows suppliers to monitor stock levels at their customers' locations and then ship replacement goods as needed. It helps organizations reduce the expenses involved with keeping an inventory, decrease the likelihood of stockouts, and increase the efficiency of their supply chains.
VMI is able to function because it creates a robust connection between the client and the supplier. It is the provider's responsibility to keep track of the quantity of stock owned at the customer's location and restock it as required. It implies that firms have a smaller selection of products since they rely on their suppliers to keep track of their inventory levels. VMI is able to aid businesses in increasing the effectiveness of their supply chains by reducing the lead times, improving the accuracy of orders, and lowering the risk of either running out of stock or having an excess inventory.
VMI is an effective technique for inventory management because it lowers the expenses of maintaining inventory while simultaneously guaranteeing that the appropriate list is available. It reduces the costs associated with inventory management when businesses rely on their suppliers to maintain inventory levels. These costs include storage, handling, and insurance. Companies see an increase in profitability and gain an advantage over their competitors.
One company that makes use of VMI is known as Procter & Gamble. Procter & Gamble uses VMI to regulate inventory levels and ensure that its products are constantly available to customers. Procter & Gamble is able to lower the expenses associated with inventory management while simultaneously boosting the efficiency of its supply chain by working closely with its suppliers to set appropriate inventory levels. Procter & Gamble saw an improvement in overall customer satisfaction and earned a competitive advantage in the market as a result.
3. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
The method is utilized to effectively handle materials and components, guaranteeing their availability for production purposes. It computes the necessary materials and components for every product by considering the production schedule and the bill of materials. Subsequently, it generates a materials plan that outlines the quantity and timing of each material that must be ordered or manufactured.
It is characterized by several essential components, including the utilization of a master production schedule (MPS) to specify the required quantity of each product, a bill of materials (BOM) to enumerate the constituents and raw materials necessary for the production of each product, and inventory data to furnish details on the overall inventory levels of each component and raw material.
The system operates through an analysis of the production schedule and the Bill of Materials (BOM) to ascertain the required materials, their respective quantities, and the appropriate timing for their procurement. The MRP system subsequently generates a comprehensive materials plan outlining the specific timing and amounts of each material that must be procured or manufactured. It is designed to monitor and regulate inventory levels and subsequently modify the materials plan in response to demand or inventory level fluctuations.
The efficacy of the MRP system is contingent upon multiple variables, such as the precision of the production timetable and Bill of Materials (BOM), the dependability of inventory information, and the enterprise's capacity to promptly adapt to fluctuations in demand. The successful implementation of MRP leads to enhanced production efficiency, decreased inventory expenses, and elevated levels of customer service for businesses.
Apple is an instance of a commercial enterprise that employs Material Requirements Planning (MRP). Apple uses Material Requirements Planning (MRP) to effectively manage its intricate supply chain and guarantee the availability of appropriate materials and components to fulfill production demands. Apple has been able to enhance its manufacturing efficiency, curtail inventory expenses, and augment its responsiveness to fluctuations in consumer demand by implementing MRP.
4. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
It is a way of supervising inventory that specifies the best number of items to buy to keep costs low while still having enough to meet customer needs. It looks at things like order costs, carrying costs, and demand rates to figure out the best amount to buy. It determines the optimal order number to keep stock costs low while ensuring enough stock to meet customer demand. It looks at things like order costs, carrying costs, and demand rates to figure out the best amount to buy. Businesses cut inventory holding costs while ensuring it has enough to meet consumer demand by estimating the ideal purchase quantity.
Its calculation is influenced by several crucial factors, namely the yearly product demand, the unit cost, and the cost incurred per order. The formula computes the most favorable inventory quantity to be ordered, considering the relevant factors, including the holding cost per unit. The holding cost denotes the expenses incurred in storing the list.
The EOQ methodology determines the most advantageous quantity of orders that reduces the overall inventory expenses, encompassing both the costs incurred in holding inventory and the fees incurred in placing orders. Ordering the most efficient quantity leads to a reduction in stock carrying costs and containing costs for businesses, ultimately resulting in substantial cost savings.
The efficacy of the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is contingent upon various factors, such as the precision of demand projections, the consistency of ordering and holding expenses, and the enterprise's agility in adapting to fluctuations in demand. The practical implementation of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) leads to reduced inventory costs and improved business profitability.
Walmart is an instance of a commercial enterprise that employs the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model. Walmart employs advanced inventory management systems to optimize customer product availability and minimize inventory expenses. Walmart is capable of procuring the most advantageous amount of merchandise to curtail the overall costs of inventory, leading to considerable financial benefits through the utilization of EOQ computations.
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a proficient inventory management methodology that facilitates enterprises in streamlining their inventory levels and curtailing expenses. Enterprises mitigate costs related to holding inventory and placing orders, enhancing profitability by computing the best quantity of goods to order. Walmart exemplifies a commercial enterprise that has efficiently executed the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, leading to substantial cost reductions and enhanced inventory administration.
5. Just-in-time (JIT) Inventory Management
It is a strategic methodology that endeavors to reduce inventory levels by generating and transporting products precisely when needed to fulfill customer demand. The Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology has found the concept of manufacturing the appropriate quantity of goods exactly when and where they are required to minimize waste, curtail lead times, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the supply chain.
The primary characteristic of JIT is its emphasis on perpetual enhancement and eradication of inefficiencies. That goal is accomplished by applying Lean manufacturing concepts, including but not limited to standardized work, visual management, and continuous flow. The Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology uses a pull-based system that relies on actual customer demand to initiate production instead of projected demand. Effective coordination and communication between suppliers and customers are imperative to ensure the optimal availability of materials and products at the appropriate time.
The efficacy of Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management is contingent upon various factors, such as the dependability of the supply chain, the degree of cooperation between suppliers and customers, and the enterprise's agility in promptly adapting to fluctuations in demand. The proper implementation of the Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology has the ability to result in noteworthy reductions in expenses, enhancements in product excellence, and heightened levels of customer contentment.
Toyota is an instance of a commercial enterprise that employs Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management. The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a renowned production system developed by Toyota, which is founded on the principles of Just-in-Time (JIT). The system has been widely acknowledged for its remarkable ability to minimize waste and enhance operational efficiency. Toyota is able to create and deliver vehicles to customers swiftly and effectively through the use of JIT while additionally lowering inventory levels and overproduction.
JIT Inventory Management is an effective strategy for businesses seeking to reduce inventory levels, decrease waste, and increase supply chain efficiency. Implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) principles improves production processes, minimizes lead times, and enables prompt responsiveness to business customer demand fluctuations. Toyota exemplifies implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management successfully, leading to notable cost reductions and enhanced operational efficacy.
What type of Inventory Management is used in Project Management?
The inventory management methodology utilized in Project Management is commonly referred to as Just-in-time (JIT) Inventory Management. The JIT methodology exhibits favorable compatibility with project management owing to its emphasis on the timely production and delivery of goods, which facilitates the fulfillment of project requirements. It has the capability to decrease the costs associated with inventory holding and improve the efficiency of the supply chain.
The JIT system functions on a pull-based paradigm, whereby the manufacturing and transportation of commodities are triggered by the authentic requisites of patrons rather than anticipated demand. It facilitates a reduction in waste and boosts project management efficiency by exclusively procuring and transporting materials and components on an as-needed basis.
The incorporation of JIT appears to be effective in the administration of project-related inventory of both materials and equipment. Assuming a given project requires a specific classification of tool or apparatus. The JIT approach ensures that the equipment is delivered to the project site precisely when needed, rather than being stored in inventory until its utilization.
The consensus is that Just-In-Time (JIT) is a very effective inventory management technique for project management since it prioritizes meeting project requirements while simultaneously minimizing inventory retention costs and oversupply. Project managers optimize supply chain efficiency, reduce expenses, and promote project effectiveness through the implementation of the Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology.
Can all types of Inventory Management be used in Project Management?
Yes, all forms of inventory management are able to be used in project management. Determining the optimal methodology for a given project is contingent upon several variables, including but not limited to the project's category, magnitude, intricacy, timeline, and inventory characteristics.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is the best inventory management strategy if a project requires many materials and components. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a tool that helps in the timely availability of appropriate materials and components to fulfill project needs. Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) is considered a suitable inventory management approach for projects that involve many suppliers and vendors. Implementing Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) assists in the synchronization and exchange of information between suppliers and vendors, guaranteeing the timely availability of materials and components.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is the best inventory management method for a project with a small storage space. The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model aids in the reduction of inventory levels, thereby mitigating the requirement for storage space and related expenses. Just-in-time (JIT) Inventory Management is the best strategy for a project with a short turnaround time and schedule. Implementing the Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology facilitates the timely delivery of materials and components, fulfilling project requisites.
Just-In-Time (JIT) is the favored inventory management approach utilized in project management. However, alternative inventory management techniques are employed based on the particular demands of the project. Determining the optimal inventory management methodology for a given project is contingent upon various considerations, including but not limited to project specifications, schedule, and inventory characteristics.
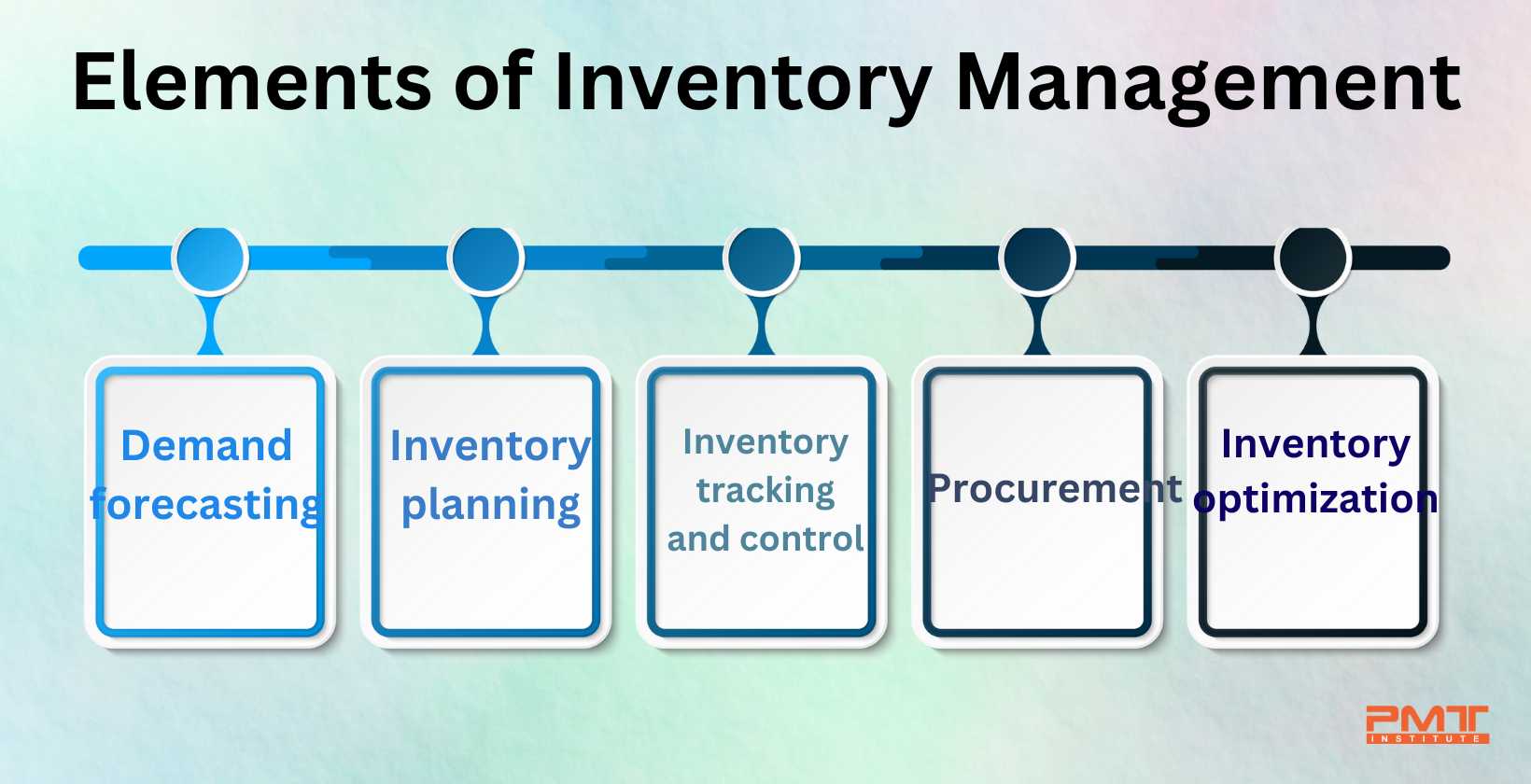
What are the Five Elements of Inventory Management?
Listed below are the five elements of inventory management.
-
Demand forecasting: Demand forecasting is the practice of estimating future consumer product demand, which aids a business in setting its inventory levels.
-
Inventory planning: Inventory planning is the process of deciding how much inventory to order or manufacture, taking into account lead times, safety stocks, and order cycles, as well as demand projections.
-
Inventory tracking and control: Inventory tracking and control is the process of keeping track of stock levels and ensuring that they are properly handled. It entails monitoring inventory movements, spotting irregularities, and modifying inventory levels as required.
-
Procurement: The process of acquiring the inventory of products required to satisfy consumer demand is known as procurement. It covers ordering from suppliers as well as delivery.
-
Inventory optimization: Efficiency and profit maximization are known as inventory optimization. It is figuring out how to lower the expenses associated with keeping inventory on hand, for example, by implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management or cutting lead times. Additionally, it entails figuring out how to raise inventory turnover, such as by implementing promotions or streamlining the manufacturing procedure.
How can Inventory Management collaborate with Quality Management?
The collaboration between inventory management and quality management aims to identify prospective areas of improvement in the inventory management process through the utilization of data and analytics. The monitoring of inventory levels and usage enables businesses to optimize their inventory levels, minimize holding expenses, and increase inventory turnover. Consequently, enterprises have the capability to enhance their overall output and financial gain.
It is imperative to engage in frequent audits, observe the quality of incoming inventory products, and take note of any flaws and nonconformities to ensure compliance with quality standards. The act of doing so aids enterprises in reducing waste and refunds, enhancing customer satisfaction, and diminishing the probability of quality issues emerging during the production phase.
Furthermore, quality management supports inventory management by recommending the appropriate inventory items required to satisfy quality criteria. Quality management assists in determining the proper type and caliber of raw materials required to produce finished goods of superior quality. Inventory management aids enterprises in maintaining optimal stock levels, reducing waste, and mitigating the risk of stock outs or overstocking.
Achieving success in any organization requires efficient coordination between inventory and quality management. Incorporating quality control protocols in inventory management mitigate production-related quality concerns, minimize waste and returns, and enhance customer contentment. Collaboratively optimizing inventory levels and improving the overall performance of inventory management procedures lead to increased profitability and a competitive edge for businesses in the market.
How often should businesses hold Inventory Management?
The number of times a business does inventory management depends on a number of things, such as the type of company, the industry, customer demand, and the suppliers' lead times. Generally, companies must perform inventory management regularly to make sure it has the right amount of inventory and reduce stockouts, overstocking, and other problems related to inventory.
Most businesses do inventory management daily, every week, or every month, based on what works best for them. Most companies that have a lot of customers and items that sell quickly use daily inventory management. These businesses need a steady inventory and must always have the right amount of inventory on hand to keep up with customer demand.
Businesses with fewer customers and things that move less quickly use weekly inventory management most of the time. These companies afford to do inventory management less often, but it is still needed to make sure they have the right amount of stock to meet customer needs and stay supplied.
Businesses with low customer demand and slow-moving inventory usually use monthly inventory management. These businesses perform it less typically because their stock stays mostly the same, and to plan their needs for stock better.
It needs to make sure it has the right tools and systems in place to do so successfully, no matter how frequently a business needs to manage its inventory. It entails inventory management software, barcoding systems, and RFID technology, which helps businesses watch inventory levels in real-time, find inventory discrepancies, and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
What are the Benefits of Inventory Management?
Listed below are the benefits of inventory management.
-
Improved cash flow: One of the primary advantages of inventory management is the enhancement of cash flow. Effective inventory management helps to free up money that is used to fund other aspects of the company's operations by lowering inventory carrying costs and avoiding overstocking.
-
Enhanced efficiency: Managing inventory well improves productivity in more than one way. It leads to faster order handling times, shorter lead times, and better on-time delivery performance. More efficient inventory management helps companies save money, provide better customer service, and make more money.
-
Cost savings: Effective inventory management helps cut costs by avoiding overstocking, stock-outs, and inventory obsolescence.
-
Increased customer satisfaction: It helps ensure that products are accessible when clients need them, enhancing client satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Better decision-making: It gives firms helpful information and insights about purchase, production, and sales choices.
-
Reduced waste: Efficient inventory management assists in reducing waste by ensuring that things are used up before they expire or become obsolete.
-
Increased competitiveness: It helps organizations become more competitive by enhancing productivity, cutting expenses, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
What are the Limitations of Inventory Management?
Listed below are the limitations of inventory management.
-
Cost: Implementing an inventory management system incurs substantial costs, including ongoing expenses for maintenance and training. To learn more about effective cost management strategies, you can read our article on cost management.
-
Complexity: Inventory management presents a considerable level of intricacy, particularly for enterprises that possess extensive and varied product portfolios or intricate supply networks.
-
Inaccurate forecasting: The effectiveness of inventory management is contingent upon precise demand forecasting, a task that proves to be challenging. It is due to the capability for inaccuracies in the forecasting process. Inaccurate predictions of demand lead to either an excess or a shortage of inventory, resulting in elevated expenses and reduced levels of customer contentment.
-
Obsolete inventory: It poses difficulties when handling items with a restricted shelf life or is susceptible to becoming obsolete.
-
Limited storage space: The management of inventory poses a challenge for businesses that have restricted storage capacity, as surplus inventory has the capability to occupy the available space rapidly.
-
Supplier reliability: The dependability of suppliers and vendors affects inventory management, as any disruptions in the supply chain caused by delays or issues with quality impact inventory levels.
-
Unexpected events: Inventory management encounters disruptions due to unforeseen circumstances, such as natural calamities, economic recessions, or disturbances in the supply chain.
What are the Challenges Inventory Management faced?
Listed below are the challenges of inventory management.
-
The precision of forecasting: The precise forecasting of demand constitutes a significant obstacle in inventory management. Inaccurate predictions have the capability to cause overstocking or stockouts, which result in elevated expenses and reduced customer contentment.
-
Disruptions to the supply chain: Natural disasters, backed-up transportation, and poor quality problems are a few factors that cause inventory management to become erratic.
-
Multiple site management: Juggling inventories between them is complex for companies with several locations.
-
Limited storage: Companies with little storage needs help to store surplus inventory, which results in higher storage costs and a higher risk of obsolescence.
-
Managing costs: It results in significant expenses, particularly for enterprises with extensive and varied product portfolios.
-
Obsolescence: Keeping track of inventory is hard when one has to deal with goods with a short shelf life or are likely to become obsolete.
-
Inaccurate data: Accurate data are essential for effective inventory management. Incorrect inventory level data results in excessive or insufficient stock.
-
Manual methods: Manual inventory management methods, such as manually counting stock or utilizing spreadsheets, are time-consuming and error-prone.
Is it important for businesses to have a clear understanding of their Inventory levels?
Yes, firms need to comprehend their inventory levels. Its effectiveness is crucial for businesses as inventory is considered one of the most significant assets. It has the capability to enhance profitability, minimize expenses, and augment customer satisfaction. Companies must understand how their inventory levels affect their operations to accomplish these goals.
It enables enterprises to make well-informed judgments regarding procurement and manufacturing. Businesses are capable of avoiding overstocking or stockouts by knowing what inventory is in stock and deciding when and how much inventory needs to be ordered. The implementation of such an approach has the capability to mitigate expenses related to inventory holding, as well as enhance production efficiency.
Accurate forecasting of demand depends on having a comprehensive grasp of inventory levels. A thorough understanding of inventory levels is necessary for precise demand forecasting since inventory influences the quantity and timing of products produced and delivered. Commercial entities generate more precise demand predictions, thereby mitigating the likelihood of excess inventory or inventory depletion by comprehending inventory levels comprehensively.
It has the capability to enhance customer satisfaction. The availability of products is a crucial factor in meeting customer expectations, as inventory shortages lead to reduced sales and diminished customer allegiance. A comprehensive comprehension of inventory levels enables businesses to guarantee product availability during customer demand, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Additionally, it is imperative to possess a comprehensive comprehension of inventory levels for financial reporting and accounting. The inventory is a crucial asset for commercial entities, and precise documentation is essential for financial reporting and taxation. Enterprises guarantee the precision of their financial statements and adhere to regulatory obligations through a comprehensive comprehension of inventory levels.
It assists enterprises in enhancing their inventory management tactics. Enterprises pinpoint opportunities for enhancement and execute alterations to improve efficacy and curtail expenses by monitoring inventory levels and analyzing inventory data. It has the capability to enhance profitability and optimize overall business performance.
A comprehensive comprehension of inventory levels is imperative for enterprises that aim to enhance profitability, curtail expenses, and augment customer contentment. A thorough understanding of inventory levels enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding procurement and production, improve the precision of demand forecasting, increase customer satisfaction, adhere to regulatory mandates, and optimize inventory management tactics.
Can poor Inventory management lead to lost sales and revenue?
Yes, poor inventory management allows firms to lose customers and money. Effective inventory management is crucial in ensuring timely availability of appropriate products to meet customer demand. Inadequate inventory management leads to stock-outs or overstocking, adversely affecting sales and revenue.
Stock-outs refer to a situation where a business is unable to fulfill customer demand due to insufficient inventory. Insufficient inventory levels decrease sales and revenue as customers purchase from rival companies with the requisite merchandise. Furthermore, the occurrence of stockouts has an adverse effect on customer loyalty, as customers experience dissatisfaction with a company that is incapable of fulfilling their product requirements in a timely manner.
Moreover, overstocking is a phenomenon that arises when a company holds surplus inventory that is not being sold. Overstocking adversely affects profitability as it leads to the immobilization of cash flow and storage space. Furthermore, excessive inventory stocking leads to obsolescence, where products that are not being sold become outdated or no longer in demand, resulting in a loss of revenue.
Additionally, inadequate inventory management practices have a negative effect on customer satisfaction. Customers expect products to be readily available when required, and any inadequacy or postponement in inventory leads to unfavorable customer encounters. The circumstance above results in a reduction in customer loyalty and a decline in revenue, as customers opt to procure goods or services from rival companies that are more proficient in satisfying their requirements.
Inadequate inventory management practices lead to escalated expenses. Maintaining excessive inventory levels results in increased expenses associated with holding inventory, whereas insufficient inventory levels lead to additional costs incurred from expedited shipping or missed sales opportunities that necessitate compensatory marketing and promotional efforts.
Inadequate management of inventory affects the overall performance of a business adversely. A business's profitability and growth are impacted by lost sales and revenue, decreased customer satisfaction, and increased costs.
Does effective Inventory Management help businesses reduce their costs?
Yes, businesses lower their costs with proper inventory management. It is an essential asset for businesses, and professional inventory management enhances profitability by mitigating expenses related to inventory holding, procurement, and production. Implementing efficient inventory management strategies improves the operational efficiency of businesses, curtails wastage, and optimizes inventory levels to minimize expenses.
Effective inventory management aids businesses in cost reduction by minimizing the expenses associated with holding inventory. Maintaining surplus inventory results in immobilizing financial resources and storage capacity, escalating costs. Efficient inventory management aids enterprises in maximizing their inventory levels and mitigating the risk of overstocking, thereby curbing the expenses incurred in holding inventory.
It helps enterprises in minimizing procurement expenses by streamlining their procurement procedures. Enterprises guarantee inventory procurement based on their requirements and at the appropriate time by identifying ideal ordering quantities and lead times. The implementation of that strategy aids in the mitigation of excessive ordering and the consequent reduction of expenses linked to procurement, including fees for orders, shipping expenses, and handling charges.
Moreover, professional inventory management has the ability to enhance the operational efficiency of enterprises by guaranteeing the availability of appropriate materials and components at the required time. The implementation of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) or Just-in-time (JIT) Inventory Management techniques leads to a reduction in inventory levels, waste minimization, and enhanced production efficiency, ultimately resulting in cost savings for businesses.
It helps enterprises in minimizing expenses linked with the obsolescence of inventory. Enterprises avert the accumulation of surplus inventory that becomes obsolete or loses its market demand through consistent inventory level assessments and identification of stagnant or outdated stock. The approach mitigates expenses linked to inventory obsolescence and diminishes wastage.
Proficient inventory management aids enterprises in curtailing expenses by streamlining inventory levels, enhancing procurement procedures, mitigating wastage, augmenting production efficacy, and diminishing the costs linked with inventory obsolescence. Implementing efficient inventory management tactics improves profitability, minimizes expenses, and optimizes the comprehensive business performance of enterprises.
Does a Project Manager oversee Inventory Management?
Yes, a Project Manager handles it in a project involving inventory production or usage. Inventory serves as a resource for creating goods or services supporting the project. Alternatively, regulating inventory quantities for the project's internal operations within project-based entities is imperative.
Project management must ensure the availability of essential materials and supplies for timely and budgeted project completion. The procurement process, which encompasses material and supply ordering, inventory level tracking, and supplier performance monitoring, falls under the purview of the Project Manager.
Furthermore, the Project Manager is responsible for supervising the creation and execution of its systems to achieve optimal inventory levels, minimize waste, and reduce costs. Optimizing inventory control and cost reduction is achieved by implementing techniques such as Just-in-time (JIT) or Material Requirements Planning (MRP).
The oversight of inventory levels and corresponding adjustments to inventory plans in response to modifications in project scope, timeline, or budget fall within the purview of the Project Manager. The task at hand requires close collaboration with project stakeholders, suppliers, and team members to ensure the adequacy of inventory levels and the efficacy of inventory management strategies.
The Project Manager's responsibilities are subject to variation based on the specific project and organizational necessities. The role of the Project Manager is crucial in maintaining optimal inventory levels to align with project goals and objectives. Additionally, the Project Manager must optimize the strategies to enhance efficiency and minimize costs.



